Experimental and in silico modelling analyses of the gene expression pathway for recombinant antibody and by-product production in NS0 cell lines
- PMID: 23071804
- PMCID: PMC3468484
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047422
Experimental and in silico modelling analyses of the gene expression pathway for recombinant antibody and by-product production in NS0 cell lines
Abstract
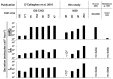
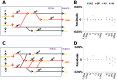
Monoclonal antibodies are commercially important, high value biotherapeutic drugs used in the treatment of a variety of diseases. These complex molecules consist of two heavy chain and two light chain polypeptides covalently linked by disulphide bonds. They are usually expressed as recombinant proteins from cultured mammalian cells, which are capable of correctly modifying, folding and assembling the polypeptide chains into the native quaternary structure. Such recombinant cell lines often vary in the amounts of product produced and in the heterogeneity of the secreted products. The biological mechanisms of this variation are not fully defined. Here we have utilised experimental and modelling strategies to characterise and define the biology underpinning product heterogeneity in cell lines exhibiting varying antibody expression levels, and then experimentally validated these models. In undertaking these studies we applied and validated biochemical (rate-constant based) and engineering (nonlinear) models of antibody expression to experimental data from four NS0 cell lines with different IgG4 secretion rates. The models predict that export of the full antibody and its fragments are intrinsically linked, and cannot therefore be manipulated individually at the level of the secretory machinery. Instead, the models highlight strategies for the manipulation at the precursor species level to increase recombinant protein yields in both high and low producing cell lines. The models also highlight cell line specific limitations in the antibody expression pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
Derivation and characterization of cholesterol-independent non-GS NS0 cell lines for production of recombinant antibodies.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2007 Feb 1;96(2):294-306. doi: 10.1002/bit.21099. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2007. PMID: 16897745
-
Functional proteomic analysis of GS-NS0 murine myeloma cell lines with varying recombinant monoclonal antibody production rate.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2006 Aug 5;94(5):830-41. doi: 10.1002/bit.20899. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2006. PMID: 16489627
-
Molecular analysis of successful cell line selection in transfected GS-NS0 myeloma cells.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2007 Feb 1;96(2):337-48. doi: 10.1002/bit.21119. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2007. PMID: 17001634
-
Proteins improving recombinant antibody production in mammalian cells.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014 Feb;98(3):1031-42. doi: 10.1007/s00253-013-5427-3. Epub 2013 Dec 11. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 24327213 Review.
-
Engineering mammalian cell factories for improved recombinant monoclonal antibody production: lessons from nature?Biotechnol Bioeng. 2005 Jul 20;91(2):180-9. doi: 10.1002/bit.20499. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2005. PMID: 15880827 Review.
Cited by
-
Engineered transient and stable overexpression of translation factors eIF3i and eIF3c in CHOK1 and HEK293 cells gives enhanced cell growth associated with increased c-Myc expression and increased recombinant protein synthesis.Metab Eng. 2020 May;59:98-105. doi: 10.1016/j.ymben.2020.02.001. Epub 2020 Feb 13. Metab Eng. 2020. PMID: 32061967 Free PMC article.
-
¹H NMR spectroscopy profiling of metabolic reprogramming of Chinese hamster ovary cells upon a temperature shift during culture.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 10;8(10):e77195. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077195. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24130854 Free PMC article.
-
Cell factory engineering: Challenges and opportunities for synthetic biology applications.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2023 Sep;120(9):2441-2459. doi: 10.1002/bit.28365. Epub 2023 Mar 11. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2023. PMID: 36859509 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Burnouf T (2011) Recombinant plasma proteins. Vox Sang 100: 68–83. - PubMed
-
- Wurm FM (2004) Production of recombinant protein therapeutics in cultivated mammalian cells. Nat Biotechnol 22: 1393–1398. - PubMed
-
- Lim Y, Wong NS, Lee YY, Ku SC, Wong DC, et al. (2010) Engineering mammalian cells in bioprocessing – current achievements and future perspectives. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 55: 175–189. - PubMed
-
- O'Callaghan PM, McLeod J, Pybus LP, Lovelady CS, Wilkinson SJ, et al. (2010) Cell line-specific control of recombinant monoclonal antibody production by CHO cells. Biotechnol Bioeng 106: 938–951. - PubMed
-
- Browne SM, Al-Rubeai M (2007) Selection methods for high-producing mammalian cell lines. Trends Biotechnol 25: 425–432. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

