The Ubiquitin Proteasome Pathway (UPP) in the regulation of cell cycle control and DNA damage repair and its implication in tumorigenesis
- PMID: 23071855
- PMCID: PMC3466981
The Ubiquitin Proteasome Pathway (UPP) in the regulation of cell cycle control and DNA damage repair and its implication in tumorigenesis
Abstract
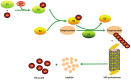
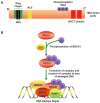
Accumulated evidence supports that the ubiquitin proteasome pathway (UPP) plays a crucial role in protein metabolism implicated in the regulation of many biological processes such as cell cycle control, DNA damage response, apoptosis, and so on. Therefore, alterations for the ubiquitin proteasome signaling or functional impairments for the ubiquitin proteasome components are involved in the etiology of many diseases, particularly in cancer development. In this minireview, we first give a brief outline for the ubiquitin proteasome pathway, we then discuss with focus for the ubiquitin proteasome pathway in the regulation of cell cycle control and DNA damage response, the relevance for the altered regulation of these signaling pathways in tumorigenesis is also reviewed. We finally assess and summarize the advancement for targeting the ubiquitin proteasome pathway in cancer therapy. A better understanding of the biological functions underlying ubiquitin regulatory mechanisms would provide us a wider prospective on cancer treatment.
Keywords: DNA damage response; Ubiquitin proteasome pathway; cell cycle; tumorigenesis; ubiquitination.
Figures

References
-
- Shah SA, Potter MW, Callery MP. Ubiquitin proteasome pathway: implications and advances in cancer therapy. Surg Oncol. 2001;10:43–52. - PubMed
-
- Ciechanover A. Intracellular protein degradation: from a vague idea thru the lysosome and the ubiquitin-proteasome system and onto human diseases and drug targeting. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1824:3–13. - PubMed
-
- Burger AM, Seth AK. The ubiquitin-mediated protein degradation pathway in cancer: therapeutic implications. Eur J Cancer. 2004;40:2217–2229. - PubMed
-
- Clague MJ, Urbe S. Ubiquitin: same molecule, different degradation pathways. Cell. 2010;143:682–685. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
