Design and development of a self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system for telmisartan for oral drug delivery
- PMID: 23071930
- PMCID: PMC3465127
- DOI: 10.4103/2230-973X.82431
Design and development of a self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system for telmisartan for oral drug delivery
Abstract
Background and aim: Telmisartan (TEL) is an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) antihypertensive agent. The aim of the present investigation was to develop a self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system (SNEDDS) to enhance the oral bioavailability of poorly water soluble TEL.
Materials and methods: The solubility of TEL in various oils was determined to identify the oil phase of a SNEDDS. Various surfactants and co-surfactants were screened for their ability to emulsify the selected oil. Pseudoternary phase diagrams were constructed to identify the efficient self-emulsifying region. A SNEDDS was further evaluated for its percentage transmittance, emulsification time, drug content, phase separation, dilution, droplet size, zeta potential, pH, refractive index, and viscosity.
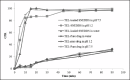
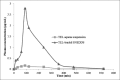
Results: The developed SNEDDS formulation contained TEL (20 mg), Tween(®) 20 (43.33%w/w), Carbitol(®) (21.67%w/w), and Acrysol(®) EL 135 (32%w/w). The optimized formulation of the TEL-loaded SNEDDS exhibited a complete in vitro drug release in 15 min as compared with the plain drug, which had a limited dissolution rate. It was also compared with the pure drug suspension by oral administration in male Wister rats. The in vivo study exhibited a 7.5-fold increase in the oral bioavailability of TEL from the SNEDDS compared with the pure drug suspension.
Conclusions: These results suggest the potential use of the SNEDDS to improve the dissolution and oral bioavailability of poorly water soluble TEL.
Keywords: Bioavailability; poor water solubility; self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system; telmisartan.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Stegemann S, Leveiller F, Franchi D, de Jong H, Lindén H. When poor solubility becomes an issue: From early stage to proof of concept. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2007;31:249–61. - PubMed
-
- Hauss DJ. Oral lipid based formulations. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2007;59:667–76. - PubMed
-
- Pouton CW. Formulation of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 1997;25:47–58.
-
- Pouton CW. Lipid formulations for oral administration of drugs: Non-emulsifying, self-emulsifying and ‘self-microemulsifying’ drug delivery systems. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2000;11:S93–8. - PubMed
-
- Pouton CW. Formulation of poorly water-soluble drugs for oral administration: Physicochemical and physiological issues and the lipid formulation classification system. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2006;29:278–87. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

