Sarcoidosis Th17 cells are ESAT-6 antigen specific but demonstrate reduced IFN-γ expression
- PMID: 23073617
- PMCID: PMC3850764
- DOI: 10.1007/s10875-012-9817-6
Sarcoidosis Th17 cells are ESAT-6 antigen specific but demonstrate reduced IFN-γ expression
Abstract
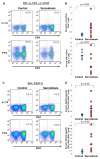
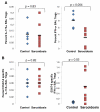
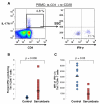
Rationale: Sarcoidosis is a granulomatous disease of unknown etiology. Many patients with sarcoidosis demonstrate antigen-specific immunity to mycobacterial virulence factors. Th-17 cells are crucial to the immune response in granulomatous inflammation, and have recently been shown to be present in greater numbers in the peripheral blood and bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid (BALF) of sarcoidosis patients than healthy controls. It is unclear whether Th-17 cells in sarcoidosis are specific for mycobacterial antigens, or whether they have similar functionality to control Th-17 cells.
Methods: Flow cytometry was used to determine the numbers of Th-17 cells present in the peripheral blood and BALF of patients with sarcoidosis, the percentage of Th-17 cells that were specific to the mycobacterial virulence factor ESAT-6, and as well as to assess IFN-γ expression in Th-17 cells following polyclonal stimulation.
Results: Patients with sarcoidosis had greater numbers of Th-17 cells in the peripheral blood and BALF than controls and produced significantly more extracellular IL-17A (p = 0.03 and p = 0.02, respectively). ESAT-6 specific Th-17 cells were present in both peripheral blood and BALF of sarcoidosis patients (p < 0.001 and p = 0.03, respectively). After polyclonal stimulation, Th-17 cells from sarcoidosis patients produced less IFN-γ than healthy controls.
Conclusions: Patients with sarcoidosis have mycobacterial antigen-specific Th-17 cells peripherally and in sites of active sarcoidosis involvement. Despite the Th1 immunophenotype of sarcoidosis immunology, the Th-17 cells have reduced IFN-γ expression, compared to healthy controls. This reduction in immunity may contribute to sarcoidosis pathogenesis.
Figures



References
-
- Zissel G, Prasse A, Muller-Quernheim J. Immunologic response of sarcoidosis. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2010;31(4):390–403. - PubMed
-
- Baughman RP, Winget DB, Bowen EH, Lower EE. Predicting respiratory failure in sarcoidosis patients. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 1997;14(2):154–8. - PubMed
-
- Facco M, Cabrelle A, Teramo A, Olivieri V, Gnoato M, Teolato S, et al. Sarcoidosis is a Th1/Th17 multisystem disorder. Thorax. 2011;66(2):144–50. - PubMed
-
- Fenoglio D, Poggi A, Catellani S, Battaglia F, Ferrera A, Setti M, et al. Vdelta1 T lymphocytes producing IFN-gamma and IL-17 are expanded in HIV-1-infected patients and respond to Candida albicans. Blood. 2009;113(26):6611–8. - PubMed
-
- Ito Y, Usui T, Kobayashi S, Iguchi-Hashimoto M, Ito H, Yoshitomi H, et al. Gamma/delta T cells are the predominant source of interleukin-17 in affected joints in collagen-induced arthritis, but not in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60(8):2294–303. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 1 UL1 RR024975/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- T35HL090555/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL83839/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 HL103179/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T35 HL090555/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32HL094296/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL094296/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32HL069765-08/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024975/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- MO1 RR-00095/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K01HL103179-01/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL112694/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 1 U01HL112694-01/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL069765/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000095/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL083839/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

