ZFIN, the Zebrafish Model Organism Database: increased support for mutants and transgenics
- PMID: 23074187
- PMCID: PMC3531097
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gks938
ZFIN, the Zebrafish Model Organism Database: increased support for mutants and transgenics
Abstract
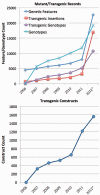
ZFIN, the Zebrafish Model Organism Database (http://zfin.org), is the central resource for zebrafish genetic, genomic, phenotypic and developmental data. ZFIN curators manually curate and integrate comprehensive data involving zebrafish genes, mutants, transgenics, phenotypes, genotypes, gene expressions, morpholinos, antibodies, anatomical structures and publications. Integrated views of these data, as well as data gathered through collaborations and data exchanges, are provided through a wide selection of web-based search forms. Among the vertebrate model organisms, zebrafish are uniquely well suited for rapid and targeted generation of mutant lines. The recent rapid production of mutants and transgenic zebrafish is making management of data associated with these resources particularly important to the research community. Here, we describe recent enhancements to ZFIN aimed at improving our support for mutant and transgenic lines, including (i) enhanced mutant/transgenic search functionality; (ii) more expressive phenotype curation methods; (iii) new downloads files and archival data access; (iv) incorporation of new data loads from laboratories undertaking large-scale generation of mutant or transgenic lines and (v) new GBrowse tracks for transgenic insertions, genes with antibodies and morpholinos.
Figures

References
-
- Busch-Nentwich E, Kettleborough R, Harvey S, Collins J, Ding M, Dooley C, Fenyes F, Gibbons R, Herd C, Mehroke S, et al. Sanger Institute Zebrafish Mutation Project phenotype and image data submission. ZFIN Direct Data Submission ( http://zfin.org/, ZDB-PUB-120207-1) 2012
-
- Ekker SC, Clark KJ, ZFIN Staff Curation of zfishbook links. ZFIN Direct Data Submission ( http://zfin.org/, ZDB-PUB-120111-1) 2012
-
- ZF-MODELS Consortium. ZF-MODELS Consortium and Zebrafish Mutation Resource targeted knock-out mutants. ZFIN Direct Data Submission ( http://zfin.org/, ZDB-PUB-070315-1) 2007

