Vascular endothelial growth factor-dependent spinogenesis underlies antidepressant-like effects of enriched environment
- PMID: 23074224
- PMCID: PMC3510798
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.392076
Vascular endothelial growth factor-dependent spinogenesis underlies antidepressant-like effects of enriched environment
Abstract
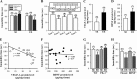
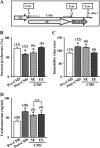
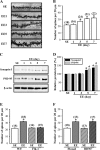
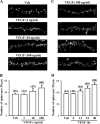
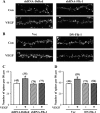
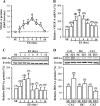
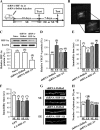
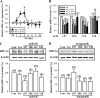
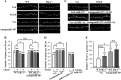
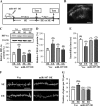
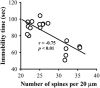
Current antidepressant treatments remain limited by poor efficacy and a slow onset of action. Increasing evidence demonstrates that enriched environment (EE) treatment can promote structural and behavioral plasticity in the brain and dampen stress-induced alterations of neuroplasticity. Here, we have examined whether short term exposure to EE is able to produce antidepressant-like effects. Our results show that housing adult mice in an EE cage for 7 days led to antidepressant-like behavioral profiles and a significant increase in the number of dendritic spines in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. These EE-induced antidepressant-like effects are primarily attributed to increased vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression through a hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α)-mediated transcriptional mechanism. Blockade of HIF-1α synthesis by lentiviral infection with HIF-1α small hairpin RNAs completely blocked the increase in expression of VEGF and the antidepressant-like effects induced by EE. Moreover, no significant antidepressant-like effects were observed with EE treatment in VEGF receptor 2 (Flk-1) knock-out mice. The increase in HIF-1α expression in the hippocampus induced by EE was associated with a decrease in endogenous levels of microRNA-107 (miR-107). Overexpression of miR-107 in the hippocampus completely blocked EE-induced HIF-1α expression and the antidepressant-like effects. These results support a model in which the down-regulation of miR-107, acting through HIF-1α, mediates VEGF-dependent spinogenesis to underlie the EE-induced antidepressant-like effects.
Figures
References
-
- Wong M. L., Licinio J. (2001) Research and treatment approaches to depression. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2, 343–351 - PubMed
-
- Kessler R. C., Berglund P., Demler O., Jin R., Koretz D., Merikangas K. R., Rush A. J., Walters E. E., Wang P. S. (2003) The epidemiology of major depressive disorder. Results from the National Comorbidity Survey Replication (NCS-R). JAMA 289, 3095–3105 - PubMed
-
- Trivedi M. H., Greer T. L., Grannemann B. D., Church T. S., Galper D. I., Sunderajan P., Wisniewski S. R., Chambliss H. O., Jordan A. N., Finley C., Carmody T. I. (2006) TREAD. Treatment with exercise augmentation for depression. Study rationale and design. Clin. Trials 3, 291–305 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

