BapE DNA endonuclease induces an apoptotic-like response to DNA damage in Caulobacter
- PMID: 23074244
- PMCID: PMC3497781
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1213332109
BapE DNA endonuclease induces an apoptotic-like response to DNA damage in Caulobacter
Abstract
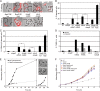
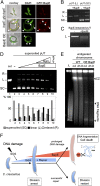
In the presence of extensive DNA damage, eukaryotes activate endonucleases to fragment their chromosomes and induce apoptotic cell death. Apoptotic-like responses have recently been described in bacteria, but primarily in specialized mutant backgrounds, and the factors responsible for DNA damage-induced chromosome fragmentation and death have not been identified. Here we find that wild-type Caulobacter cells induce apoptotic-like cell death in response to extensive DNA damage. The bacterial apoptosis endonuclease (BapE) protein is induced by damage but not involved in DNA repair itself, and mediates this cell fate decision. BapE fragments chromosomes by cleaving supercoiled DNA in a sequence-nonspecific manner, thereby perturbing chromosome integrity both in vivo and in vitro. This damage-induced chromosome fragmentation pathway resembles that of eukaryotic apoptosis. We propose that damage-induced programmed cell death can be a primary stress response for some bacterial species, providing isogenic bacterial communities with advantages similar to those that apoptosis provides to multicellular organisms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Comment in
-
Bacterial physiology: Caulobacter chooses to self-destruct.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2012 Dec;10(12):802-3. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2913. Epub 2012 Nov 13. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 23147704 No abstract available.
References
-
- Vousden KH. Outcomes of p53 activation—spoilt for choice. J Cell Sci. 2006;119(Pt 24):5015–5020. - PubMed
-
- Lakin ND, Jackson SP. Regulation of p53 in response to DNA damage. Oncogene. 1999;18(53):7644–7655. - PubMed
-
- Little JW, Mount DW. The SOS regulatory system of Escherichia coli. Cell. 1982;29(1):11–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

