Metal-on-metal hip resurfacing arthroplasty: an analysis of safety and revision rates
- PMID: 23074429
- PMCID: PMC3440005
Metal-on-metal hip resurfacing arthroplasty: an analysis of safety and revision rates
Abstract
Background: Metal-on-metal (MOM) hip resurfacing arthroplasty (HRA) is in clinical use as an appropriate alternative to total hip arthroplasty in young patients. In this technique, a metal cap is placed on the femoral head to cover the damaged surface of the bone and a metal cup is placed in the acetabulum.
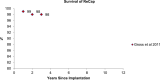
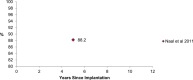
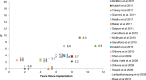
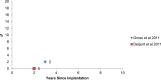
Objectives: The primary objective of this analysis was to compare the revision rates of MOM HRA using different implants with the benchmark set by the National Institute of Clinical Excellence (NICE). The secondary objective of this analysis was to review the literature regarding adverse biological effects associated with implant material.
Review methods: A literature search was performed on February 13, 2012, to identify studies published from January 1, 2009, to February 13, 2012.
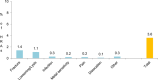
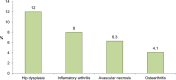
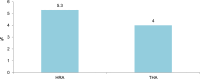
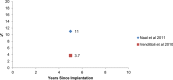
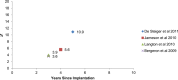
Results: The revision rates for MOM HRA using 6 different implants were reviewed. The revision rates for MOM HRA with 3 implants met the NICE criteria, i.e., a revision rate of 10% or less at 10 years. Two implants had short-term follow-ups and MOM HRA with one of the implants failed to meet the NICE criteria. Adverse tissue reactions resulting in failure of the implants have been reported by several studies. With a better understanding of the factors that influence the wear rate of the implants, adverse tissue reactions and subsequent implant failure can be minimized. Many authors have suggested that patient selection and surgical technique affect the wear rate and the risk of tissue reactions. The biological effects of high metal ion levels in the blood and urine of patients with MOM HRA implants are not known. Studies have shown an increase in chromosomal aberrations in patients with MOM articulations, but the clinical implications and long-term consequences of this increase are still unknown. Epidemiological studies have shown that patients with MOM HRA implants did not have an overall increase in mortality or risk of cancer. There is insufficient clinical data to confirm the teratogenicity of MOM implants in humans.
Conclusions: Metal-on-metal HRA can be beneficial for appropriately selected patients, provided the surgeon has the surgical skills required for performing this procedure.
Figures





References
-
- National Institute of Clinical Excellence Guidance on the selection of prostheses for primary total hip replacement. [[updated 2000 Apr; cited 2012 Mar 3]]. (Technology appraisal guidance No 2) [Internet]. London: NICE. 9p. Available from: http://www.nice.org.uk/nicemedia/live/11386/32002/32002.pdf .
-
- Murphy TP, Trousdale RT, Pagnano MW, Mabry TM, Sierra RJ. Patients’ perceptions of hip resurfacing arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 2009 Oct;32(10) - PubMed
-
- Klein GR, Levine BR, Hozack WJ, Strauss EJ, D’Antonio JA, Macaulay W, et al. Return to athletic activity after total hip arthroplasty. Consensus guidelines based on a survey of the Hip Society and American Association of Hip and Knee Surgeons. J Arthroplasty. 2007 Feb;22(2):171–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
