Laminin α5 guides tissue patterning and organogenesis
- PMID: 23076210
- PMCID: PMC3544791
- DOI: 10.4161/cam.22236
Laminin α5 guides tissue patterning and organogenesis
Abstract
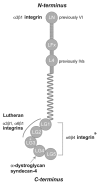
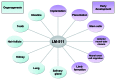
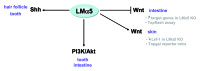
Laminins (LM) are extracellular matrix molecules that contribute to and are required for the formation of basement membranes. They participate in the modulation of epithelial/mesenchymal interactions and are implicated in organogenesis and maintenance of organ homeostasis. Among the LM molecules, the LM α5 chain (LMα5) is one of the most widely distributed LM in the developing and mature organism. Its presence in some basement membranes during embryogenesis is absolutely required for maintenance of basement membrane integrity and thus for proper organogenesis. LMα5 also regulates the expression of genes important for major biological processes, in part by repressing or activating signaling pathways, depending upon the physiological context.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
