Hyperbaric oxygen for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss and tinnitus
- PMID: 23076907
- PMCID: PMC11561530
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004739.pub4
Hyperbaric oxygen for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss and tinnitus
Abstract
Background: This is an update of a Cochrane Review first published in The Cochrane Library in Issue 1, 2005 and previously updated in 2007 and 2009.Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss (ISSHL) is common and has a significant effect on quality of life. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) may improve oxygen supply to the inner ear and result in an improvement in hearing.
Objectives: To assess the benefits and harms of HBOT for treating ISSHL and/or tinnitus.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Ear, Nose and Throat Disorders Group Trials Register; the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL); PubMed; EMBASE; Database of Randomised Trials in Hyperbaric Medicine (DORCTHIM); CINAHL; Web of Science; BIOSIS Previews; Cambridge Scientific Abstracts; ICTRP and additional sources for published and unpublished trials. The date of the most recent search was 2 May 2012, following previous searches in 2009, 2007 and 2004.
Selection criteria: Randomised studies comparing the effect on ISSHL and tinnitus of HBOT and alternative therapies.
Data collection and analysis: Three authors evaluated the quality of trials using the 'Risk of bias' tool and extracted data from the included trials.
Main results: Seven trials contributed to this review (392 participants). The studies were small and of generally poor quality. Pooled data from two trials did not show any significant improvement in the chance of a 50% increase in hearing threshold on pure-tone average with HBOT (risk ratio (RR) with HBOT 1.53, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.85 to 2.78, P = 0.16), but did show a significantly increased chance of a 25% increase in pure-tone average (RR 1.39, 95% CI 1.05 to 1.84, P = 0.02). There was a 22% greater chance of improvement with HBOT, and the number needed to treat (NNT) to achieve one extra good outcome was 5 (95% CI 3 to 20). There was also an absolute improvement in average pure-tone audiometric threshold following HBOT (mean difference (MD) 15.6 dB greater with HBOT, 95% CI 1.5 to 29.8, P = 0.03). The significance of any improvement in tinnitus could not be assessed.There were no significant improvements in hearing or tinnitus reported for chronic presentation (six months) of ISSHL and/or tinnitus.
Authors' conclusions: For people with acute ISSHL, the application of HBOT significantly improved hearing, but the clinical significance remains unclear. We could not assess the effect of HBOT on tinnitus by pooled analysis. In view of the modest number of patients, methodological shortcomings and poor reporting, this result should be interpreted cautiously. An appropriately powered trial is justified to define those patients (if any) who can be expected to derive most benefit from HBOT.There is no evidence of a beneficial effect of HBOT on chronic ISSHL or tinnitus and we do not recommend the use of HBOT for this purpose.
Conflict of interest statement
None known.
Figures
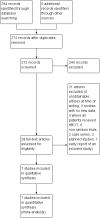


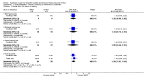








Update of
-
Hyperbaric oxygen for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss and tinnitus.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Jan 24;(1):CD004739. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004739.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Oct 17;10:CD004739. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004739.pub4. PMID: 17253520 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Cavallazzi 1996 {published data only}
-
- Cavallazzi G, Pignataro L, Capaccio P. Italian experience in hyperbaric oxygen therapy for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Proceedings of the International Joint Meeting on Hyperbaric and Underwater Medicine. Bologna: Grafica Victoria, 1996:647‐9.
Fattori 2001 {published data only}
-
- Fattori B, Berrettini S, Casani A, Nacci A, Vito A, Iaco G. Sudden hypoacusis treated with hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Ear Nose and Throat Journal 2001;80(9):655‐60. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hoffmann 1995a {published data only}
-
- Desloovere C, Knecht R, Bohmer D, Hoffmann G. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy by chronic tinnitus ‐ a double‐blind study [Hyperbare Sauerstofftherapie bei chronischem Tinnitus ‐ Eine Doppelblind‐Studie]. European Archives of Oto‐Rhino‐Laryngology 1993;Suppl 2:225‐6.
-
- Hoffmann G, Bohmer D, Desloovere C. Hyperbaric oxygenation as a treatment of chronic forms of inner ear hearing loss and tinnitus. Proceedings of the Eleventh International Congress on Hyperbaric Medicine. Flagstaff, Az: Best Publishing, 1995:141‐5.
Hoffmann 1995b {published data only}
-
- Hoffmann G, Bohmer D, Desloovere C. Hyperbaric oxygenation as a treatment for sudden deafness and acute tinnitus. Proceedings of the Eleventh International Congress on Hyperbaric Medicine. Flagstaff, Az: Best Publishing, 1995:146‐51.
Pilgramm 1985 {published data only}
-
- Pilgramm M, Lamm H, Schumann K. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy in sudden deafness [Zur hyperbaren Sauerstofftherapie beim Hörsturz]. Laryngologie, Rhinologie, Otologie 1985;64(7):351‐4. - PubMed
Schwab 1998 {published data only}
-
- Schwab B, Flunkert C, Heermann R, Lenarz T. HBO in the therapy of cochlear dysfunctions ‐ first results of a randomized study. EUBS Diving and Hyperbaric Medicine, Collected manuscripts of XXIV Annual Scientific Meeting of the European Underwater and Baromedical Society. Stockholm: EUBS, 1998:40‐2.
Topuz 2004 {published data only}
-
- Topuz E, Yigit O, Cinar U, Seven H. Should hyperbaric oxygen be added to treatment in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss?. European Archives of Oto‐Rhino‐Laryngology 2004;261(7):393‐6. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Blagovesh 1990 {published data only}
-
- Blagoveshchenskaia NS. Treatment and prevention of acute sensorineural hearing loss. Vestnik Otorinolaringologii 1990;6:4‐12. - PubMed
Cuixia 2008 {published data only}
-
- Cuixia X, Xinli Z, Lin W. Clinical observation of hyperbaric oxygen and ginaton in the treatment of sudden deafness. 16th International Congress on Hyperbaric Medicine. 2008.
Dauman 1993 {published data only}
-
- Dauman R, Poisot D, Cros AM, Zennaro O, Bertrand B, Duclos JY, et al. Sudden hearing loss: comparative randomized study of two modalities of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in association with naftidrofuryl [Surdites brusques: etude comparative randomisee de deux modes d'administration de l'oxygenotherapie hyperbare associee au naftidrofuryl]. Revue de Laryngologie 1993;114(1):53‐8. - PubMed
Dundar 2007 {published data only}
-
- Dundar K, Gumus T, Ay H, Yetiser S, Ertugrul E. Effectiveness of hyperbaric oxygen on sudden sensorineural hearing loss: prospective clinical research. Journal of Otolaryngology 2007;36(1):32‐7. - PubMed
Joachims 1978 {published data only}
-
- Joachims HZ, Monies‐Chass I, Eliachar I. Hyperbaric oxygen in the treatment of sudden deafness. Harefuah 1978;95(7):202‐3. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lamm 1995 {published data only}
-
- Lamm H. The influence of hyperbaric oxygen therapy on tinnitus and hearing loss in acute and chronic inner ear damage. Oto‐Rhino‐Laryngologia Nova 1995;5:3‐4. [SN 1014‐8221]
Lamm 1998 {published data only}
-
- Lamm K, Lamm H, Arnold W. Effect of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in comparison to conventional or placebo therapy or no treatment in idiopathic sudden hearing loss, acoustic trauma, noise‐induced hearing loss and tinnitus. A literature survey. Advances in Otorhinolaryngology 1998;54:86‐99. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Li 2010 {published data only}
-
- Li Z, Yang H, Xiao Y, Wu Y, Yang J, Li Z. Curative effect analysis of hyperbaric oxygen and medication in the treatment of sudden hearing loss. China Modern Medicine 2010;8:1.
Lina 2010 {published data only}
-
- Lina H, Zhaowen Y, Yuqin D. An effective appraisal of hyperbaric oxygen combined with drugs therapy for sudden deafness. Journal of Shantou University Medical College 2001;1:1.
Sano 1988 {published data only}
-
- Sano H, Okamoto M, Hirayama M, Ono Y, Nitta M. Hearing recovery in sudden deafness with profound hearing loss. Nippon Jibiinkoka Gakkai Kaiho 1988;101(6):836‐40. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sparacia 2003 {published data only}
-
- Sparacia B, Sparacia G. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy in treatment of sudden deafness. Acta Medica Mediterranea 2003;19(2):95‐102. [SN 0393‐6384]
Tisch 2000 {published data only}
-
- Tisch M, Maier H. Acute tinnitus ‐ reperfusion therapy versus hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Notfall Medizin 2000;26:1‐2. [SN 0341‐2903]
Wang 2000 {published data only}
-
- Wang W, Xu R, Lu R, Yan Y. A reappraisal of hyperbaric oxygenation effect and study on serum malondialdehyde and superoxide dismutase in patients with sudden deafness. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Ke Za Zhi 2000;35(5):356‐8. - PubMed
Xiao 1986 {published data only}
-
- Xiao ZX. Comparative analysis of the therapeutic effect of HBO and HBO combined with vasodilator agents in 200 cases of deafness. Journal of Hyperbaric Medicine 1986;1:192‐3.
References to studies awaiting assessment
Assenova 2012 {published data only}
-
- Assenova K. Hyperbaric oxygenation for treatment of hearing loss and tinnitus. 83rd Annual Meeting of the German Society of Oto‐Rhino‐Laryngology, Head and Neck Surgery. 2012.
Gui‐lian 2009 {published data only}
-
- Gui‐lian J. Clinical observation of batroxobin combined acupuncture point and hyperbaric oxygen to treat sudden deafness. Hebei Medicine 2009; Vol. 6.
Nie 2007 {published data only}
-
- Nie C, Tang M. Hyperbaric oxygen therapeutics in treatment of sudden hearing loss. Chinese Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine 2007;6:1.
Qiao 2006 {published data only}
-
- Qiao X, Zhang H. Clinical observation of hyperbaric oxygen and ginaton in the treatment of sudden deafness. Journal of Otolaryngology and Ophthalmology of Shandong University 2006; Vol. 5.
References to ongoing studies
Barthelemy 2002 {published data only}
-
- Barthélémy A, Germonpré P, Heiden C, Jansen E, Rocco M. Hyperbaric oxygen in the treatment of sudden deafness after failure of previous medical treatment start up of a multicentric, prospective and randomised study. http://gtuem.praesentiert‐ihnen.de/tools/literaturdb/project2/pdf/2002_P04%20Barthelemy.pdf 2002.
Bennett 2010 {published data only}
-
- Bennett MH, Kertesz T, Lehm JP. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for sudden sensorineural hearing loss. http://www.anzctr.org.au/trial_view.aspx?id=308282 2010 (accessed 11 July 2012). [ACTRN12609000619246]
Additional references
Agarwal 2009
ATA 2001
-
- American Tinnitus Association. Website of the American Tinnitus Association. http://www.ata.org/ (accessed April 2004).
Baldo 2006
Belal 1980
-
- Belal A. Pathology of vascular sensorineural hearing impairment. Laryngoscope 1980;90:1831‐9. - PubMed
Cacace 2003
-
- Cacace AT. Expanding the biological basis of tinnitus: crossmodal origins and the role of neuroplasticity. Hearing Research 2003;175(1‐2):112‐32. - PubMed
Coles 1990
-
- Coles DA, Davis AC. Tinnitus: its epidemiology and management. 14th Danavox Jubilee Foundation, Copenhagen. 1990.
Dauman 1992
-
- Dauman R, Tyler RS. Some considerations on the classification of tinnitus. Proceedings of the Fourth International Tinnitus Seminar, Bordeaux. 1992:225‐9.
Haberkamp 1999
-
- Haberkamp TJ, Tanyeri HM. The management of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. American Journal of Otolaryngology 1999;20:587‐92. - PubMed
Handbook 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Hughes 1996
-
- Hughes GB, Freedman MA, Haberkamp TJ, Guay ME. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otolaryngologic Clinics of North America 1996;29:393‐405. - PubMed
Jastreboff 1990
-
- Jastreboff PJ. Phantom auditory perception (tinnitus): mechanisms of generation and perception. Neuroscience Research 1990;8(4):221‐54. - PubMed
Kaltenbach 2000
-
- Kaltenbach JA. Neurophysiologic mechanisms of tinnitus. Journal of the American Academy of Audiology 2000;11(3):125‐37. - PubMed
Khan 2003
-
- Khan B, Evans AW, Easterbrook M. Refractive changes in patients undergoing hyperbaric oxygen therapy: a prospective study. Undersea and Hyperbaric Medicine 2003;24(Suppl):9.
Luxon 1993
Mattox 1977
-
- Mattox DE, Simmons FB. Natural history of sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Annals of Otolaryngology, Rhinolaryngology and Laryngology 1977;86(4):463‐80. - PubMed
Noell 2003
-
- Noell CA, Meyerhoff WL. Tinnitus. Diagnosis and treatment of this elusive symptom. Geriatrics 2003;58(2):28‐34. - PubMed
Parnes 1997
-
- Parnes SM. Current concepts in the clinical management of patients with tinnitus. European Archives of Otorhinolaryngology 1997;254:406‐9. - PubMed
RevMan 2011 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.1. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011.
Stephens 1991
-
- Stephens D, Hetu R. Impairment, disability and handicap in audiology: towards a consensus. Audiology 1991;30:185‐200. - PubMed
Stokroos 1996a
-
- Stokroos RJ, Albers FW, Cauwenberge P. Diagnosis and treatment of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss (ISSHL): a survey in the Netherlands and Flanders. Acta Otorhinolaryngologica Belgica 1996;50:237‐45. - PubMed
Sullivan 1992
-
- Sullivan M, Katon WJ, Russo J, Dobie R, Sakai C. Somatization, co‐morbidity, and the quality of life: measuring the effect of depression upon chronic medical illness. Psychiatric Medicine 1992;10(3):61‐76. - PubMed
Sullivan 1994
-
- Sullivan M, Katon W, Russo J, Dobie R, Sakai C. Coping and marital support as correlates of tinnitus disability. General Hospital Psychiatry 1994;16(4):259‐66. - PubMed
Thurmond 1998
-
- Thurmond M, Amedee RG. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss: etiologies and treatments. Journal of the Louisiana State Medical Society 1998;150(5):200‐3. - PubMed
Yoon 1990
-
- Yoon TH, Paparella MM, Schachern PA, Alleva M. Histopathology of sudden hearing loss. Laryngoscope 1990;100(7):707‐15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

