Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) for uterine leiomyomas
- PMID: 23076912
- PMCID: PMC12186162
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD005287.pub4
Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) for uterine leiomyomas
Abstract
Background: Uterine fibroids are benign tumours that arise from individual smooth muscle cells of the uterus. Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) are estrogen receptor (ER) ligands that act as estrogens in some tissues while blocking estrogen activity in others. There have been many clinical studies of various SERMs for uterine fibroids. However, their effectiveness is controversial.
Objectives: To evaluate the effectiveness and safety of selective estrogen receptor modulators in women with uterine fibroids.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Menstrual Disorders and Subfertility Group Trials Register, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), MEDLINE, PubMed, EMBASE, the Register of Chinese trials developed by the Chinese Cochrane Centre, and the Chinese Med Database (Chinese Biomedical Disc), VIP, and China National Knowledge Infrastructure. We handsearched a number of journals and searched reference lists, and searched databases of ongoing trials and the Internet. The searches were conducted in March and April 2012.
Selection criteria: We included randomised controlled studies of selective estrogen receptor modulators versus other forms of medical therapy, placebo or no treatment in women of reproductive age (18 to 45 years old) with confirmed uterine fibroids.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently extracted data and assessed trial quality. As the studies identified were not sufficiently similar, we did not do a meta-analysis but summarised the data in a narrative format.
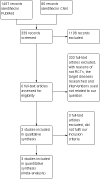
Main results: Three studies involving 215 participants were included, the trial size varied from 25 to 100 women. The SERM in all cases was raloxifene. In one study women in both arms received gonadotrophin releasing hormone (GnRH) analogue. Comparison interventions included no treatment and placebo. Two of the three included studies found a significant benefit from raloxifene, but the third study found no benefit at three or six-month follow-up. The overall quality of the evidence was low or very low. All three studies mentioned adverse reactions but data were limited.
Authors' conclusions: There is no consistent evidence from the limited number of studies that SERMs reduce the size of fibroids or improve clinical outcomes. Further studies are required to establish evidence of benefit of SERMs in treating women with uterine fibroids. This updated review did not find any new study for inclusion.
Conflict of interest statement
None known
Figures








Update of
-
Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) for uterine leiomyomas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Oct 17;(4):CD005287. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005287.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Oct 17;10:CD005287. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005287.pub4. PMID: 17943846 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Jirecek 2004 {published data only}
-
- Jirecek S, Lee A, Pavo I, Crans G, Eppel W, Wenzl R. Raloxifene prevents the growth of uterine leiomyomas in premenopausal women. Fertility and Sterility 2004;81(1):132‐6. [MEDLINE: ; CN‐00464250] - PubMed
Palomba 2002 {published data only}
-
- Palomba S, Orio F Jr, Morelli M, Russo T, Pellicano M, Zupi E, et al. Raloxifene administration in premenopausal women with uterine leiomyomas: A pilot study. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 2002;87(8):3603‐8. [MEDLINE: ; CN‐00390670] - PubMed
Palomba 2002a {published data only}
-
- Palomba S, Russo T, Orio F Jr, Tauchmanova L, Zupi E, Panici PL, et al. Effectiveness of combined GnRH analogue plus raloxifene administration in the treatment of uterine leiomyomas: a prospective, randomized, single‐blind, placebo‐controlled clinical trial. Human Reproduction 2002;17(12):3213‐9. [MEDLINE: ; CN‐00419275] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Palomba 2001 {published data only}
-
- Palomba S, Sammartino A, Carlo C, Affinito P, Zullo F, Nappi C. Effects of raloxifene treatment on uterine leiomyomas in postmenopausal women. Fertility and Sterility 2001;76(1):38‐43. - PubMed
Palomba 2002b {published data only}
-
- Palomba S, Orio F Jr, Morelli M, Russo T, Pellicano M, Nappi C. Raloxifene administration in women treated with gonadotropin‐releasing hormone agonist for uterine leiomyomas: effects on bone metabolism. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 2002;87(10):4476‐81. - PubMed
Palomba 2004 {published data only}
-
- Palomba S, Orio F Jr, Morelli M, Russo T, Pellicano M, Nappi C. Lipid, glucose and homocysteine metabolism in women treated with a GnRH agonist with or without raloxifene. Human Reproduction 2004;19(2):415‐21. - PubMed
Additional references
Borgfeldt 2000
-
- Borgfeldt C, Andolf E. Transvaginal ultrasonographic findings in the uterus and the endometrium: low prevalence of leiomyoma in a random sample of women age 25‐40 years. Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica 2000;79(3):202‐7. - PubMed
Boss 1997
-
- Boss SM, Huster WJ, Neild JA, Glant MD, Eisenhunt CC, Draper MW. Effects of raloxifene hydrochloride on the endometrium of postmenopausal women. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1997;177:1458‐64. - PubMed
Buttram 1981
-
- Buttram VC Jr, Reiter RC. Uterine leiomyomas: Etiology, symptomology, and management. Fertility and Sterility 1981;36:433‐45. - PubMed
CONSORT 2010
-
- Schulz KF, Altman DG, Moher D. CONSORT 2010 Statement: updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials. BMJ (http://www.bmj.com/content/340/bmj.c332.full) 2010; Vol. 340, issue c332. - PMC - PubMed
Davies 1999
-
- Davies GC, Huster WJ, Lu Y, Plouffe L Jr, Lakshmanan M. Adverse events reported by postmenopausal women in controlled trials with raloxifene. Obstetrics and Gynecology 1999;93(4):558‐65. - PubMed
Delmas 1997
-
- Delmas PD, Bjarnason NH, Mitlak BH, Ravoux AC, Shah AS, Huster WJ, et al. Effects of raloxifene on bone mineral density, serum cholesterol concentrations, and uterine endometrium in postmenopausal women. The New England Journal of Medicine 1997;337:1641‐7. - PubMed
Draper 1996
-
- Draper MW, Flowers DE, Huster WJ, Neild JA, Harper KD, Arnaud C. A controlled trial of raloxifene HCl (LY139481): impact on bone turnover and serum lipid profile in healthy postmenopausal women. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research 1996;11:835‐42. - PubMed
Dutertre 2000
-
- Dutertre M, Smith C. Molecular mechanisms of selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) action. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 2000;295(2):431‐7. - PubMed
Egger 1997
Eli Lilly 1997
-
- Eli Lilly, Company. Indianapolis. Raloxifene. Package insert 1997.
Ettingrr 1999
-
- Ettingrr B, Black DM, Mitlak BH, et al. Reduction of vertebral fracture risk in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis treated with raloxifene. JAMA 1999;282:637‐45. - PubMed
Farber 1972
-
- Farber M, Conrad S, Heinrichs NL, Herrman WL. Estradiol binding by fibroid tumours and normal myometrium. Obstetrics and Gynecology 1972;40:479‐83. - PubMed
Goldstein 2002
-
- Goldstein SR, Nanavati N. Adverse events that are associated with the selective estrogen receptor modulator levormeloxifene in an aborted phase III osteoporosis treatment study. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2002;187(3):521‐7. - PubMed
Gustafsson 1999
-
- Gustafsson J‐A. Estrogen receptor beta a new dimension in estrogen mechanism of action. Journal of Endocrinology 1999;163:379‐83. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011.
Lethaby 2002
-
- Lethaby A, Vollenhoven B. Fibroids. Clinical Evidence 2002;8:1666‐78. - PubMed
Matta 1989
-
- Matta WHM, Shaw RW, Nye M. Long‐term follow‐up of patients with uterine fibroids after treatment with the LHRH agonist buserelin. British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 1989;96:200‐6. - PubMed
Mitlak 1997
-
- Mitlak BH, Cohen FJ. In search of optimal long‐term female hormone replacement: the potential of selective estrogen receptor modulators. Hormone Research 1997;48:155‐63. - PubMed
Otubu 1982
-
- Otubu JA, Buttrum VC, Besch NF, Besch PK. Unconjugated steroids in leiomyomas and tumor‐bearing myometrium. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1982;143:130‐3. - PubMed
Ravina 1995
-
- Ravina JH, Herbreteau D, Ciraru‐Vigneron N, Bouret J, Houdart E, Aymard A, et al. Arterial embolisation to treat uterine myomata. The Lancet 1995;346:671‐2. - PubMed
Scott 1990
-
- Scott JA, Camara CC, Early JE. Raloxifene: A selective estrogen receptor modulator. American Family Physician 1990;60(4):1131‐9. - PubMed
Stewart 1992
-
- Stewart EA, Friedman AJ. Steroidal treatment of myomas: preoperative and long term medical therapy. Seminars in Reproductive Endocrinology 1992;10:344‐57.
Tamaya 1985
-
- Tamaya T, Fujimoto J, Okada H. Comparison of cellular levels of steroid receptors in uterine leiomyomas and myometrium. Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica 1985;64:307‐9. - PubMed
Vercellini 1993
-
- Vercellini P, Vendola N, Ragni G, Trespidi L, Oldani S, Crosignani PG. Abnormal uterine bleeding associated with iron‐deficiency anaemia: Etiology and role of hysteroscopy. Journal of Reproductive Medicine 1993;38:502‐4. - PubMed
Vollenhoven 1994
-
- Vollenhoven BJ, Pearce P, Herington AC, Healy DL. Steroid receptor binding and messenger RNA expression in fibroids from untreated and gonadotrophin‐releasing hormone agonist pretreated women. Clinical Endocrinology 1994;40(4):537‐44. - PubMed
Wilson 1980
-
- Wilson EA, Yang F, Rees ED. Estradiol and progesterone binding in uterine leiomyomata and in normal uterine tissue. Obstetrics and Gynecology 1980;55:20‐4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

