Interventions for oropharyngeal dysphagia in children with neurological impairment
- PMID: 23076958
- PMCID: PMC11654901
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009456.pub2
Interventions for oropharyngeal dysphagia in children with neurological impairment
Abstract
Background: Oropharyngeal dysphagia encompasses problems with the oral preparatory phase of swallowing (chewing and preparing the food), oral phase (moving the food or fluid posteriorly through the oral cavity with the tongue into the back of the throat) and pharyngeal phase (swallowing the food or fluid and moving it through the pharynx to the oesophagus). Populations of children with neurological impairment who commonly experience dysphagia include, but are not limited to, those with acquired brain impairment (for example, cerebral palsy, traumatic brain injury, stroke), genetic syndromes (for example, Down syndrome, Rett syndrome) and degenerative conditions (for example, myotonic dystrophy).
Objectives: To examine the effectiveness of interventions for oropharyngeal dysphagia in children with neurological impairment.
Search methods: We searched the following electronic databases in October 2011: CENTRAL 2011(3), MEDLINE (1948 to September Week 4 2011), EMBASE (1980 to 2011 Week 40) , CINAHL (1937 to current) , ERIC (1966 to current), PsycINFO (1806 to October Week 1 2011), Science Citation Index (1970 to 7 October 2011), Social Science Citation Index (1970 to 7 October 2011), Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 2011(3), DARE 2011(3), Current Controlled Trials (ISRCTN Register) (15 October 2011), ClinicalTrials.gov (15 October 2011) and WHO ICTRP (15 October 2011). We searched for dissertations and theses using Networked Digital Library of Theses and Dissertations, Australasian Digital Theses Program and DART-Europe E-theses Portal (11 October 2011). Finally, additional references were also obtained from reference lists from articles.
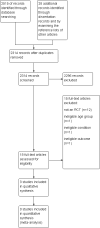
Selection criteria: The review included randomised controlled trials and quasi-randomised controlled trials for children with oropharyngeal dysphagia and neurological impairment.
Data collection and analysis: All three review authors (AM, PD and EW) independently screened titles and abstracts for inclusion and discussed results. In cases of uncertainty over whether an abstract met inclusion criterion, review authors obtained the full-text article and independently evaluated each paper for inclusion. The data were categorised for comparisons depending on the nature of the control group (for example, oral sensorimotor treatment versus no treatment). Effectiveness of the oropharyngeal dysphagia intervention was assessed by considering primary outcomes of physiological functions of the oropharyngeal mechanism for swallowing (for example, lip seal maintenance), the presence of chest infection and pneumonia, and diet consistency a child is able to consume. Secondary outcomes were changes in growth, child's level of participation in the mealtime routine and the level of parent or carer stress associated with feeding.
Main results: Three studies met the inclusion criteria for the review. Two studies were based on oral sensorimotor interventions for participants with cerebral palsy compared to standard care and a third study trialled lip strengthening exercises for children with myotonic dystrophy type 1 compared to no treatment (Sjogreen 2010). A meta-analysis combining results across the three studies was not possible because one of the studies had participants with a different condition, and the remaining two, although using oral sensorimotor treatments, used vastly different approaches with different intensities and durations. The decision not to combine these was in line with our protocol. In this review, we present the results from individual studies for four outcomes: physiological functions of the oropharyngeal mechanism for swallowing, the presence of chest infection and pneumonia, diet consistency, and changes in growth. However, it is not possible to reach definitive conclusions on the effectiveness of particular interventions for oropharyngeal dysphagia based on these studies. One study had a high risk of attrition bias owing to missing data, had statistically significant differences (in weight) across experimental and control groups at baseline, and did not describe other aspects of the trial sufficiently to enable assessment of other potential risks of bias. Another study was at high risk of detection bias as some outcomes were assessed by parents who knew whether their child was in the intervention or control group. The third study overall seemed to be at low risk of bias, but like the other two studies, suffered from a small sample size.
Authors' conclusions: The review demonstrates that there is currently insufficient high-quality evidence from randomised controlled trials or quasi-randomised controlled trials to provide conclusive results about the effectiveness of any particular type of oral-motor therapy for children with neurological impairment. There is an urgent need for larger-scale (appropriately statistically powered), randomised trials to evaluate the efficacy of interventions for oropharyngeal dysphagia.
Conflict of interest statement
Angela T Morgan ‐ none known.
Elizabeth C Ward ‐ none known.
Pamela Dodrill ‐ none known.
Figures
Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Gisel 1996b {published and unpublished data}
-
- Gisel EG. Effect of oral sensorimotor treatment on measures of growth and efficiency of eating in the moderately eating‐impaired child with Cerebral Palsy. Dysphagia 1996;11:48‐58. - PubMed
Ottenbacher 1981 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Ottenbacher K, Scoggins A, Wayland J. The effectiveness of a program of oral sensory motor therapy with the severely and profoundly disabled. Occupational Therapy Journal of Research 1981;1(2):147‐60.
Sjogreen 2010 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Sjogreen L, Tulinius M, Kiliaridis S, Lohmander A. The effect of lip strengthening exercises in children and adolescents with myotonic dystrophy type 1. International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology 2010;74:1126–34. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Alacam 2007 {published data only}
-
- Alacam A, Kolcuoǧlu N. Effects of two types of appliances on orofacial dysfunctions of disabled children. The British Journal of Developmental Disabilities (BJDD) 2007;35(2):111‐23.
Arvedson 2010 {published data only}
-
- Arvedson J, Clark H, Lazarus C, Schooling T, Frymark T. The effects of oral‐motor exercises on swallowing in children: an evidence‐based systematic review. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology 2010;19(4):321‐40. - PubMed
Christiaanse 2011 {published data only}
-
- Christiaanse ME, Mabe B, Russell G, Long Simeone T, Fortunato J, Rubin B. Neuromuscular electrical stimulation is no more effective than usual care for the treatment of primary dysphagia in children. Pediatric Pulmonology 2011;46:559–65. - PubMed
DeMatteo 2002 {published data only}
-
- DeMatteo C, Law M, Goldsmith C. The effect of food textures on intake by mouth and the recovery of oral motor function in the child with a severe brain injury. Physical & Occupational Therapy in Pediatrics 2002;22(3/4):51‐71. - PubMed
Ganz 1987 {published data only}
-
- Ganz SF. Decreasing tongue thrusting and tonic bite reflex through neuromotor and sensory facilitation techniques. Physical and Occupational Therapy in Pediatrics 1987;7(4):57‐75.
Gisel 1996a {published data only}
-
- Gisel EG, Applegate‐Ferrante T, Benson J, Bosma JF. Oral‐motor skills following sensorimotor therapy in two groups of moderately dysphagic children with cerebral palsy: aspiration vs nonaspiration. Dysphagia 1996;11:59‐71. - PubMed
Gisel 2001 {published data only}
-
- Gisel EG. Impact of oral appliance therapy: are oral skills and growth maintained one year after termination of therapy?. Dysphagia 2001;16:296‐307. - PubMed
Haberfellner 2001 {published data only}
-
- Haberfellner H, Schwartz S, Gisel E. Feeding skills and growth after one year of intraoral appliance therapy in moderately dysphagic children with cerebral palsy. Dysphagia 2001;16:83‐96. - PubMed
Iammatteo 1990 {published data only}
-
- Iammatteo PA, Trombly C, Luecke L. The effect of mouth closure on drooling and speech. The American Journal of Occupational Therapy 1990;44(8):686‐91. - PubMed
Kiger 2006 {published data only}
-
- Kiger M, Brown CS, Watkins L. Dysphagia management: an analysis of patient outcomes using VitalStim therapy compared to traditional swallow therapy. Dysphagia 2006;21(4):243‐53. - PubMed
Korbmacher 2004 {published data only}
-
- Korbmacher HM, Schwan M, Berndsen S, Bull J, Kahl‐Nieke B. Evaluation of a new concept of myofunctional therapy in children. International Journal of Orofacial Myology 2004;30:39‐52. - PubMed
Ottenbacher 1983 {published data only}
-
- Ottenbacher K, Hicks J, Roark A, Swinea J. Oral sensorimotor therapy in the developmentally disabled: a multiple baseline study. American Journal of Occupational Therapy 1983;37:541‐7. - PubMed
Pinnington 1999 {published data only}
-
- Pinnington L, Hegarty J. Effects of consistent food presentation on efficiency of eating and nutritive value of food consumed by children with severe neurological impairment. Dysphagia 1999;14:17‐26. - PubMed
Pinnington 2000 {published data only}
-
- Pinnington L, Hegarty J. Effects of consistent food presentation on oral‐motor skill acquisition in children with severe neurological impairment. Dysphagia 2000;15:213–23. - PubMed
Sobsey 1984 {published data only}
-
- Sobsey R, Orelove FP. Neurophysiological facilitation of eating skills in children with severe handicaps. Journal of the Association for Persons with Severe Handicaps 1984;9(2):98‐110.
Additional references
Arrowsmith 2006
-
- Arrowsmith FE, Allen JR, Gaskin KJ, Gruca MA, Clarke SL, Briody JN, et al. Reduced body protein in children with spastic quadriplegic cerebral palsy. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2006;83:613‐8. - PubMed
Arvedson 1994
-
- Arvedson J, Rogers B, Buck G, Smart P, Msall M. Silent aspiration prominent in children with dysphagia. International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology 1994;28:173‐81. - PubMed
Arvedson 2008
-
- Arvedson JC. Assessment of pediatric dysphagia and feeding disorders: clinical and instrumental approaches. Developmental Disabilities Research Reviews 2008;14:118‐27. - PubMed
Ball 2012
-
- Ball SL, Panter SG, Redley M, Proctor CA, Byrne K, Clare IC, et al. The extent and nature of need for mealtime support among adults with intellectual disabilities. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research 2011;56(4):382‐401. - PubMed
Calis 2008
-
- Calis EAC, Veugelers R, Sheppard JJ, Tibboel D, Evenhuis HM, Penning C. Dysphagia in children with severe generalized cerebral palsy and intellectual disability. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology 2008;50(8):625‐30. - PubMed
Chadwick 2003
-
- Chadwick DD, Jolliffe J, Goldbart J. Adherence to eating and drinking guidelines for adults with intellectual disabilities and dysphagia. American Journal of Mental Retardation 2003;108(3):202‐11. - PubMed
Cherney 2012
Cook 1989
-
- Cook IJ, Dodds WJ, Dantas RO, Massey B, Kern MK, Lang IM, et al. Opening mechanisms of the human upper esophageal sphincter. The American Journal of Physiology 1989;257:G748‐59. - PubMed
Cornwell 2003
-
- Cornwell PL, Murdoch BE, Ward EC, Morgan AT. Dysarthria and dysphagia as long‐term sequelae in a child treated for recurrent posterior fossa tumour. Pediatric Rehabilitation (now known as Developmental Neurorehabilitation) 2003;6(2):67‐75. - PubMed
Farmer 2001
-
- Farmer JE, Muhlenbruch L. Telehealth for children with special health care needs: promoting comprehensive systems of care. Clinical Pediatrics 2001;40(2):93‐8. - PubMed
Faulks 2007
-
- Faulks D, Collado V, Mazille MN, Veyrune JL, Hennequin M. Masticatory dysfunction in persons with Down's syndrome. Part 1: aetiology and incidence. Journal of Oral Rehabilitation 2008;35(11):854‐62. - PubMed
Gallander 1979
-
- Gallander D. Eating handicaps: illustrated techniques for feeding disorders.. Eating Handicaps: Illustrated Techniques For Feeding Disorders. Springfield, Illinois: Charles CThomas Pub Ltd, 1979.
Gallander 1980
-
- Gallander D. Teaching Eating and Toileting Skills to the Multi‐handicapped in the School Setting. Springfield, Illinois: Charles C Thomas Pub Ltd, 1980.
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (Editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Huckabee 1999
-
- Huckabee ML, Cannito MP. Outcomes of swallowing rehabilitation in chronic brainstem dysphagia: a retrospective evaluation. Dysphagia 1999;14:93‐109. - PubMed
Jennett 2003
-
- Jennett PA, Affleck Hall L, Hailey D, Ohinmaa A, Anderson C, Thomas R, et al. The socio‐economic impact of telehealth: a systematic review. Journal of Telemedicine and Telecare 2003;9(6):311‐20. - PubMed
Jones 2012
-
- Jones CJ, Bryant‐Waugh R. Development and pilot of a group skills‐and‐support intervention for mothers of children with feeding problems. Appetite 2012;58(2):450‐6. - PubMed
Kleim 2008
-
- Kleim JA, Jones TA. Principles of experience‐dependent neural plasticity: implications for rehabilitation after brain damage. Journal of Speech, Language and Hearing Research 2008;51(1):S225‐39. - PubMed
Larnert 1995
-
- Larnert G, Ekberg O. Positioning improves the oral and pharyngeal swallowing function in children with cerebral palsy. Acta Paediatrica 1995;84(6):689‐92. - PubMed
Lazarus 1993
-
- Lazarus C, Logemann JA, Rademaker AW, Kahrilas PJ, Pajak T, Lazar R, et al. Effects of bolus volume, viscosity and repeated swallows in nonstroke subjects and stroke patients. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 1993;74:1066‐70. - PubMed
Lazzara 1986
-
- Lazzara G, Lazarus C, Logemann JA. Impact of thermal stimulation on the triggering of the swallow reflex. Dysphagia 1986;1:73‐7.
Lefebvre 2008
-
- Lefebvre C, Manheinmer E, Glanville J. Chapter 6: Searching for studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors) Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.0.1 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Logemann 1991
-
- Logemann J. Approaches to management of disordered swallowing. Bailliere's Clinical Gastroenterology 1991;5(2):269‐80. - PubMed
Logemann 1993
-
- Logemann JA. Noninvasive approaches to deglutitive aspiration. Dysphagia 1993;8(4):331‐3. - PubMed
Logemann 1995
-
- Logemann JA, Pauloski BR, Colangelo L, Lazarus C, Fujiu M, Kahrilas PJ. Effects of a sour bolus on oropharyngeal swallowing measures in patients with neurogenic dysphagia. Journal of Speech and Hearing Research 1995;383:556‐63. - PubMed
Loughlin 1989
-
- Loughlin GM. Respiratory consequences of dysfunctional swallowing and aspiration. Dysphagia 1989;3:126‐30. - PubMed
Morgan 2003
-
- Morgan AT, Ward E, Murdoch B, Kennedy B, Murison R. Incidence, characteristics and predictive factors for dysphagia following paediatric traumatic brain injury. Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation 2003;18(3):239‐51. - PubMed
Morgan 2004
-
- Morgan A, Ward E, Murdoch B. A case study of the resolution of paediatric dysphagia following brainstem injury: clinical and instrumental assessment. Journal of Clinical Neuroscience 2004;11(2):182‐90. - PubMed
Morgan 2010a
-
- Morgan AT. Dysphagia in childhood traumatic brain injury: a reflection on the evidence and its implications for practice. Developmental Neurorehabilitation 2010;13(3):192‐203. - PubMed
Morgan 2010b
-
- Morgan AT, Mageandran SD, Mei C. Incidence and clinical presentation of dysarthria and dysphagia in the acute setting following paediatric traumatic brain injury. Child: Care, Health and Development 2010;36(1):44‐53. - PubMed
Morton 1997
-
- Morton RE, Bonas R, Minford J, Kerr A, Ellis RE. Feeding ability in Rett syndrome. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology 1997;39(5):331‐5. - PubMed
Ohmae 1996
-
- Ohmae Y, Logemann JA, Kaiser P, Hanson DG, Kahrilas PJ. Effects of two breath‐holding maneuvers on oropharyngeal swallow. Annals of Otology, Rhinology and Laryngology 1996;105:123‐31. - PubMed
Packman 2012
-
- Packman A, Onslow M. Investigating optimal intervention intensity with the Lidcombe Program of early stuttering intervention. International Journal of Speech‐Language Pathology July 2012;E‐pub ahead of print. - PubMed
Patrick 1990
-
- Patrick J, Gisel EJ. Nutrition for the feeding impaired child. Journal of Neurology & Rehabilitation 1990;4:115‐9.
Philpot 1999
Redstone 2004
-
- Redstone F, West JF. The importance of postural control for feeding. Pediatric Nursing 2004;30(2):97‐100. - PubMed
Reilly 1996
-
- Reilly S, Skuse D, Poblete X. Prevalence of feeding problems and oral motor dysfunction in children with cerebral palsy: a community survey. Journal of Pediatrics 1996;129(6):877‐82. - PubMed
Robbins 2007
-
- Robbins J, Kays SA, Gangnon RE, Hind JA, Hewitt AL, Gentry LR, et al. The effects of lingual exercise in stroke patients with dysphagia. Archives of Physical Medicine Rehabilitation 2007;88(2):150‐8. - PubMed
Rosenbloom 1996
-
- Rosenbloom L, Sullivan P, editors. Feeding the Disabled Child. Clinics in Developmental Medicine. Vol. 140, London: Mac Keith Press, 1996.
Stallings 1993
-
- Stallings VA, Charney EB, Davies JC, Cronk CE. Nutrition related growth failure of children with quadriplegic cerebral palsy. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology 1993;35:126‐38. - PubMed
Thommessan 1991
-
- Thommessan M, Heiberg A, Kase BF, Larsen S, Riis G. Feeding problems, height and weight in different groups of disabled children. Acta Paediatrica Scandinavica 1991;80(5):527‐33. - PubMed
Veness 2008
-
- Veness C, Reilly S. Mealtime interaction patterns between young children with cerebral palsy and their mothers: characteristics and relationship to feeding impairment. Child Care Health Development 2008;34(6):815‐24. - PubMed
Vulpe 1977
-
- Vulpe SG. Vulpe Assessment Battery. 2nd Edition. Toronto: Canadian Association for Retarded Citizens, 1977.
Wade 2012
-
- Wade VA, Eliott JA, Hiller JE. A qualitative study of ethical, medico‐legal and clinical governance matters in Australian telehealth services. Journal of Telemedicine and Telecare 2012;18(2):109‐14. - PubMed
WHO 2001
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF). Geneva: World Health Organization 2001.
Williams 2012
-
- Williams AL. Intensity in phonological intervention: is there a prescribed amount?. International Journal of Speech‐Language Pathology July 2012;E‐pub ahead of print. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous