High density lipoprotein biogenesis, cholesterol efflux, and immune cell function
- PMID: 23077142
- PMCID: PMC3793253
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.300135
High density lipoprotein biogenesis, cholesterol efflux, and immune cell function
Abstract
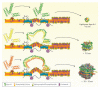
This review provides a summary of recent research on the role of high-density lipoprotein (HDL)/apolipoprotein A-I cholesterol efflux and immune cell function. Plasma concentrations of HDL have been known to inversely correlate with risk for coronary vascular disease. Bulk transport of HDL cholesterol from the peripheral tissues to the liver is a major pathway, termed reverse cholesterol transport, responsible for maintaining whole body cholesterol homeostasis. In addition to participating in this pathway, HDL and apolipoprotein A-I exert anti-inflammatory effects through different pathways. One pathway that seems to be important in atherosclerosis and autoimmunity is its role in modulation of T cell activation. HDL/apolipoprotein A-I helps regulate cell signaling by accepting membrane cholesterol from ATP binding cassette transporter A1 on immune cells and, thereby, fine tuning the amount of cholesterol present in plasma membrane lipid rafts.
Figures
References
-
- Castelli WP, Doyle JT, Gordon T, Hames CG, Hjortland MC, Hulley SB, Kagan A, Zukel WJ. HDL cholesterol and other lipids in coronary heart disease. The cooperative lipoprotein phenotyping study. Circulation. 1977;55:767–772. - PubMed
-
- Duffy D, Rader DJ. Update on strategies to increase HDL quantity and function. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2009;6:455–463. - PubMed
-
- Brown WV, Brewer HB, Rader DJ, Schaefer EJ. HDL as a treatment target. J Clin Lipidol. 2010;4:5–16. - PubMed
-
- Francis GA. The complexity of HDL. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1801:1286–1293. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

