Sensitive troponins--which suits better for hemodialysis patients? Associated factors and prediction of mortality
- PMID: 23077650
- PMCID: PMC3471860
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047610
Sensitive troponins--which suits better for hemodialysis patients? Associated factors and prediction of mortality
Abstract
Background: In hemodialysis patients, elevated plasma troponin concentrations are a common finding that has even increased with the advent of newly developed sensitive assays. However, the interpretation and relevance of this is still under debate.
Methods: In this cross-sectional study, we analyzed plasma concentrations of sensitive troponin I (TnI) and troponin T (TnT) in stable ambulatory hemodialysis patients (n = 239) and investigated their associations with clinical factors and mortality.
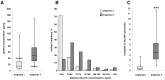
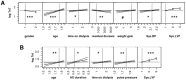
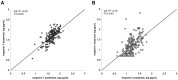
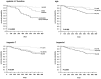
Results: In all of the enrolled patients, plasma TnI or TnT was detectable at a median concentration of 14 pg/ml (interquartile range: 7-29) using the Siemens TnI ultra assay and 49 pg/ml (31-74) using the Roche Elecsys high sensitive TnT assay. Markedly more patients exceeded the 99th percentile for TnT than for TnI (95% vs. 14%, p<0.0001). In a multivariate linear regression model, TnT was independently associated with age, gender, systolic dysfunction, time on dialysis, residual diuresis and systolic blood pressure, whereas TnI was independently associated with age, systolic dysfunction, pulse pressure, time on dialysis and duration of a HD session. During a follow-up period of nearly two years, TnT concentration above 38 pg/mL was associated with a 5-fold risk of death, whereas elevation of TnI had a gradual association to mortality.
Conclusion: In hemodialysis patients, elevations of plasma troponin concentrations are explained by cardiac function and dialysis-related parameters, which contribute to cardiac strain. Both are highly predictive of increased risk of death.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prognostic value of troponin T, troponin I, and CK-MBmass in patients with chronic renal failure.Med Klin (Munich). 2003 Apr 15;98(4):188-92. doi: 10.1007/s00063-003-1243-3. Med Klin (Munich). 2003. PMID: 12715142
-
[Diagnostic and differential diagnostic value of troponins].Med Klin (Munich). 1996 Jun 15;91(6):336-42. Med Klin (Munich). 1996. PMID: 8767305 German.
-
Influence of sampling time and ultrafiltration coefficient of the dialysis membrane on cardiac troponin I and T.Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2008 Jan;132(1):72-6. doi: 10.5858/2008-132-72-IOSTAU. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2008. PMID: 18181677
-
Effect of Remote Ischemic Preconditioning on Outcomes in Adult Cardiac Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Studies.Anesth Analg. 2018 Jul;127(1):30-38. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000002674. Anesth Analg. 2018. PMID: 29210794
-
Cardiac-specific troponins in uncomplicated pregnancy and pre-eclampsia: A systematic review.PLoS One. 2021 Feb 26;16(2):e0247946. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0247946. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33635922 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Variability of high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T and I in asymptomatic patients receiving hemodialysis.Sci Rep. 2021 Aug 30;11(1):17334. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-96658-0. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34462456 Free PMC article.
-
Optimal Cutoff Levels of More Sensitive Cardiac Troponin Assays for the Early Diagnosis of Myocardial Infarction in Patients With Renal Dysfunction.Circulation. 2015 Jun 9;131(23):2041-50. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.014245. Epub 2015 May 6. Circulation. 2015. PMID: 25948542 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic values of high sensitivity cardiac troponin T and I for long-term mortality in hemodialysis patients.Sci Rep. 2022 Aug 17;12(1):13929. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-17799-4. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35977974 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value and link to atrial fibrillation of soluble Klotho and FGF23 in hemodialysis patients.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 3;9(7):e100688. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100688. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24991914 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Discordance of High-Sensitivity Troponin Assays in Patients With Suspected Acute Coronary Syndromes.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021 Mar 30;77(12):1487-1499. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2021.01.046. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 33766254 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wu AH, Ford L (1999) Release of cardiac troponin in acute coronary syndromes: ischemia or necrosis? Clin Chim Acta 284: 161–174. - PubMed
-
- Thygesen K, Alpert JS, White HD (2007) Universal definition of myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J 28: 2525–2538. - PubMed
-
- Freda BJ, Tang WH, Van Lente F, Peacock WF, Francis GS (2002) Cardiac troponins in renal insufficiency: review and clinical implications. J Am Coll Cardiol 40: 2065–2071. - PubMed
-
- Artunc F, Haap M, Heyne N, Weyrich P, Wolf S (2010) [Interpretation of elevated serum troponin levels in end stage renal disease – case 2/2010]. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 135: 240. - PubMed
-
- Katus HA, Haller C, Muller-Bardorff M, Scheffold T, Remppis A (1995) Cardiac troponin T in end-stage renal disease patients undergoing chronic maintenance hemodialysis. Clin Chem 41: 1201–1203. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

