In vivo kinematics of high-flex mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasty, with a new post-cam design, in deep knee bending motion
- PMID: 23081946
- PMCID: PMC3508061
- DOI: 10.1007/s00264-012-1673-8
In vivo kinematics of high-flex mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasty, with a new post-cam design, in deep knee bending motion
Abstract
Purpose: The objective of this study was to evaluate the in vivo knee kinematics to assess the available functional motion of the characteristic mobile-bearing prosthesis design and to examine whether the artificial joint would work in vivo according to its design concept.
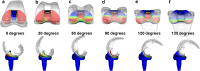
Methods: We studied 14 knees (11 patients) implanted with the Vanguard RP Hi-Flex prosthesis. This prosthesis has a highly original form of post-cam called a PS saddle design with high compatibility, and with a rotating plate mobile-bearing mechanism. The cylinder-type post-cam is designed to enable contact in early flexion ranges, and to prevent paradoxical anterior femoral component movement. Each patient performed weight-bearing deep knee bending under fluoroscopic surveillance. Motion between each component including the polyethylene insert was analyzed using the 2D/3D registration technique.
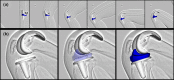
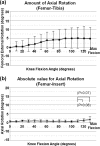
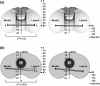
Results: The mean range of motion was 122.0°. The mean femoral component rotation for the tibial tray was 5.0°. No paradoxical anterior movement of the nearest point was confirmed between the femoral component and the tibial tray in the early flexion ranges. Initial contact of the post-cam was confirmed at a knee flexion angle of 33.8°. Subsequently, the wide contact of the post-cam was maintained until flexion reached 120° in all knees, but disengagement of the post-cam was observed in two knees when flexion was ≥130°.
Conclusions: The results of this study demonstrated that the prosthesis design generally works in vivo as intended by its design concept. The present kinematic data may provide useful information for improvement of high-flex type prostheses.
Figures
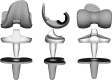
Similar articles
-
In vivo kinematics of mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasty during deep knee bending under weight-bearing conditions.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011 Jun;19(6):914-20. doi: 10.1007/s00167-010-1262-6. Epub 2010 Sep 16. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011. PMID: 20845031
-
In vivo determination of cam-post engagement in fixed and mobile-bearing TKA.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014 Jan;472(1):254-62. doi: 10.1007/s11999-013-3257-3. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014. PMID: 23990448 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo kinematics comparison of fixed- and mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasty during deep knee bending motion.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014 Jul;22(7):1612-8. doi: 10.1007/s00167-012-2333-7. Epub 2012 Dec 12. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014. PMID: 23232786
-
Do high flexion posterior stabilised total knee arthroplasty designs increase knee flexion? A meta analysis.Int Orthop. 2011 Sep;35(9):1309-19. doi: 10.1007/s00264-011-1228-4. Epub 2011 Mar 16. Int Orthop. 2011. PMID: 21409370 Free PMC article.
-
Biomechanical considerations in the design of high-flexion total knee replacements.ScientificWorldJournal. 2014;2014:205375. doi: 10.1155/2014/205375. Epub 2014 May 6. ScientificWorldJournal. 2014. PMID: 24892040 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mobile-bearing insert used with total knee arthroplasty does not rotate on the tibial tray during a squatting activity: a cross-sectional study.J Orthop Surg Res. 2020 Mar 20;15(1):114. doi: 10.1186/s13018-020-1570-6. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020. PMID: 32197628 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Are the long term results of a high-flex total knee replacement affected by the range of flexion?Int Orthop. 2014 Apr;38(4):761-6. doi: 10.1007/s00264-013-2179-8. Epub 2013 Nov 28. Int Orthop. 2014. PMID: 24287979 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of in vivo polyethylene wear particles between mobile- and fixed-bearing TKA in the same patients.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017 Sep;25(9):2887-2893. doi: 10.1007/s00167-016-4027-z. Epub 2016 Feb 4. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017. PMID: 26846659
-
Fracture of the insert cone of a polyethylene liner in a failed posterior-stabilized, rotating-platform total knee arthroplasty.Arthroplast Today. 2017 Nov 7;4(2):148-152. doi: 10.1016/j.artd.2017.10.002. eCollection 2018 Jun. Arthroplast Today. 2017. PMID: 29896543 Free PMC article.
-
Bi-cruciate substituting total knee arthroplasty improved medio-lateral instability in mid-flexion range.J Orthop. 2017 Jan 7;14(1):201-206. doi: 10.1016/j.jor.2016.12.005. eCollection 2017 Mar. J Orthop. 2017. PMID: 28123262 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sorrells RB, Voorhorst PE, Murphy JA, Bauschka MP, Greenwald AS. Uncemented rotating-platform total knee replacement: a five to twelve-year follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86:2156–2162. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

