The angiogenic factor secretoneurin induces coronary angiogenesis in a model of myocardial infarction by stimulation of vascular endothelial growth factor signaling in endothelial cells
- PMID: 23081990
- PMCID: PMC3839617
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.076950
The angiogenic factor secretoneurin induces coronary angiogenesis in a model of myocardial infarction by stimulation of vascular endothelial growth factor signaling in endothelial cells
Abstract
Background: Secretoneurin is a neuropeptide located in nerve fibers along blood vessels, is upregulated by hypoxia, and induces angiogenesis. We tested the hypothesis that secretoneurin gene therapy exerts beneficial effects in a rat model of myocardial infarction and evaluated the mechanism of action on coronary endothelial cells.
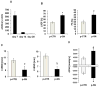
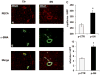
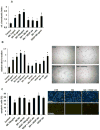
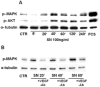
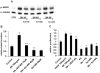
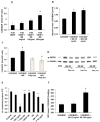
Methods and results: In vivo secretoneurin improved left ventricular function, inhibited remodeling, and reduced scar formation. In the infarct border zone, secretoneurin induced coronary angiogenesis, as shown by increased density of capillaries and arteries. In vitro secretoneurin induced capillary tubes, stimulated proliferation, inhibited apoptosis, and activated Akt and extracellular signal-regulated kinase in coronary endothelial cells. Effects were abrogated by a vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) antibody, and secretoneurin stimulated VEGF receptors in these cells. Secretoneurin furthermore increased binding of VEGF to endothelial cells, and binding was blocked by heparinase, indicating that secretoneurin stimulates binding of VEGF to heparan sulfate proteoglycan binding sites. Additionally, secretoneurin increased binding of VEGF to its coreceptor neuropilin-1. In endothelial cells, secretoneurin also stimulated fibroblast growth factor receptor-3 and insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor, and in coronary vascular smooth muscle cells, we observed stimulation of VEGF receptor-1 and fibroblast growth factor receptor-3. Exposure of cardiac myocytes to hypoxia and ischemic heart after myocardial infarction revealed increased secretoneurin messenger RNA and protein.
Conclusions: Our data show that secretoneurin acts as an endogenous stimulator of VEGF signaling in coronary endothelial cells by enhancing binding of VEGF to low-affinity binding sites and neuropilin-1 and stimulates further growth factor receptors like fibroblast growth factor receptor-3. Our in vivo findings indicate that secretoneurin may be a promising therapeutic tool in ischemic heart disease.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Hypoxia up-regulates the angiogenic cytokine secretoneurin via an HIF-1alpha- and basic FGF-dependent pathway in muscle cells.FASEB J. 2007 Sep;21(11):2906-17. doi: 10.1096/fj.06-7440com. Epub 2007 May 15. FASEB J. 2007. PMID: 17504977
-
Gene therapy with the angiogenic cytokine secretoneurin induces therapeutic angiogenesis by a nitric oxide-dependent mechanism.Circ Res. 2009 Nov 6;105(10):994-1002. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.199513. Epub 2009 Oct 1. Circ Res. 2009. PMID: 19797703
-
The neuropeptide secretoneurin acts as a direct angiogenic cytokine in vitro and in vivo.Circulation. 2004 Feb 17;109(6):777-83. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000112574.07422.C1. Circulation. 2004. PMID: 14970115
-
Signaling transduction mechanisms mediating biological actions of the vascular endothelial growth factor family.Cardiovasc Res. 2001 Feb 16;49(3):568-81. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6363(00)00268-6. Cardiovasc Res. 2001. PMID: 11166270 Review.
-
Fibroblast growth factor regulation of neovascularization.Curr Opin Hematol. 2008 May;15(3):215-20. doi: 10.1097/MOH.0b013e3282f97d98. Curr Opin Hematol. 2008. PMID: 18391788 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
OSM Enhances Angiogenesis and Improves Cardiac Function after Myocardial Infarction.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:317905. doi: 10.1155/2015/317905. Epub 2015 Jun 4. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26146616 Free PMC article.
-
Secretoneurin to the Rescue?: Maybe or Maybe Not.Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2019 Apr;12(4):e007298. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.119.007298. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2019. PMID: 30943764 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Fasting before or after wound injury accelerates wound healing through the activation of pro-angiogenic SMOC1 and SCG2.Theranostics. 2020 Feb 19;10(8):3779-3792. doi: 10.7150/thno.44115. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32206122 Free PMC article.
-
Serum levels of chromogranins and secretogranins correlate with the progress and severity of Parkinson's disease.Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2019 Mar;35(3):146-150. doi: 10.1002/kjm2.12026. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 30887724 Free PMC article.
-
Alcohol consumption negates estrogen-mediated myocardial repair in ovariectomized mice by inhibiting endothelial progenitor cell mobilization and function.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jun 21;288(25):18022-34. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.468009. Epub 2013 May 3. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23645678 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gheorghiade M, Bonow RO. Chronic heart failure in the united states: A manifestation of coronary artery disease. Circulation. 1998;97:282–289. - PubMed
-
- Kawamoto A, Murayama T, Kusano K, Ii M, Tkebuchava T, Shintani S, Iwakura A, Johnson I, von Samson P, Hanley A, Gavin M, Curry C, Silver M, Ma H, Kearney M, Losordo DW. Synergistic effect of bone marrow mobilization and vascular endothelial growth factor-2 gene therapy in myocardial ischemia. Circulation. 2004;110:1398–1405. - PubMed
-
- Kondo I, Ohmori K, Oshita A, Takeuchi H, Fuke S, Shinomiya K, Noma T, Namba T, Kohno M. Treatment of acute myocardial infarction by hepatocyte growth factor gene transfer: The first demonstration of myocardial transfer of a “functional” gene using ultrasonic microbubble destruction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;44:644–653. - PubMed
-
- Kusano KF, Pola R, Murayama T, Curry C, Kawamoto A, Iwakura A, Shintani S, Ii M, Asai J, Tkebuchava T, Thorne T, Takenaka H, Aikawa R, Goukassian D, von Samson P, Hamada H, Yoon YS, Silver M, Eaton E, Ma H, Heyd L, Kearney M, Munger W, Porter JA, Kishore R, Losordo DW. Sonic hedgehog myocardial gene therapy: Tissue repair through transient reconstitution of embryonic signaling. Nat Med. 2005;11:1197–1204. - PubMed
-
- Yanagisawa-Miwa A, Uchida Y, Nakamura F, Tomaru T, Kido H, Kamijo T, Sugimoto T, Kaji K, Utsuyama M, Kurashima C, Ito H. Salvage of infarcted myocardium by angiogenic action of basic fibroblast growth factor. Science. 1992;257:1401–1403. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

