Involvement of CXCR4 chemokine receptor in metastastic HER2-positive esophageal cancer
- PMID: 23082154
- PMCID: PMC3474831
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047287
Involvement of CXCR4 chemokine receptor in metastastic HER2-positive esophageal cancer
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2013;8(5). doi: 10.1371/annotation/5dafa9a8-2e6d-4487-b35f-7126141fe00e doi: 10.1371/annotation/5dafa9a8-2e6d-4487-b35f-7126141fe00e
Abstract
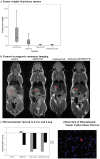
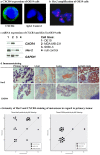
A functional linkage of the structurally unrelated receptors HER2 and CXCR4 has been suggested for breast cancer but has not been evaluated for esophageal carcinoma. The inhibition of HER2 leads to a reduction of primary tumor growth and metastases in an orthotopic model of esophageal carcinoma. The chemokine receptor CXCR4 has been implicated in metastatic dissemination of various tumors and correlates with poor survival in esophageal carcinoma. The aim of this study was to investigate a correlation between the expression levels of HER2 and CXCR4 and to evaluate the involvement of CXCR4-expression in HER2-positive esophageal carcinoma. The effects of HER2-inhibition with trastuzumab and of CXCR4-inhibition with AMD3100 on primary tumor growth, metastatic homing, and receptor expression were evaluated in vitro and in an orthotopic model of metastatic esophageal carcinoma using MRI for imaging. The clinical relevance of HER2- and CXCR4-expression was examined in esophageal carcinoma patients. A significant correlation of HER2- and CXCR4-expression in primary tumor and metastases exists in the orthotopic model. Trastuzumab and AMD3100 treatment led to a significant reduction of primary tumor growth, metastases and micrometastases. HER2-expression was significantly elevated under AMD3100 treatment in the primary tumor and particularly in the metastases. The positive correlation between HER2- and CXCR4-expression was validated in esophageal cancer patients. The correlation of CXCR4- and HER2-expression and the elevation of HER2-expression and reduction of metastases through CXCR4-inhibition suggest a possible functional linkage and a role in tumor dissemination in HER2-positive esophageal carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Yarden Y (2001) The EGFR family and its ligands in human cancer. signalling mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Eur J Cancer 37 Suppl 4 S3–S8. - PubMed
-
- Zhang D, Salto-Tellez M, Do E, Putti TC, Koay ES (2003) Evaluation of HER-2/neu oncogene status in breast tumors on tissue microarrays. Hum Pathol 34: 362–368. - PubMed
-
- Slamon DJ, Clark GM, Wong SG, Levin WJ, Ullrich A, et al. (1987) Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science 235: 177–182. - PubMed
-
- Yu D, Hung MC (2000) Role of erbB2 in breast cancer chemosensitivity. Bioessays 22: 673–680. - PubMed
-
- al-Kasspooles M, Moore JH, Orringer MB, Beer DG (1993) Amplification and over-expression of the EGFR and erbB-2 genes in human esophageal adenocarcinomas. Int J Cancer 54: 213–219. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

