Successful treatment of long-term severe progressive interstitial pneumonia with low-dose corticosteroid and azathioprine in a patient with diffuse systemic sclerosis
- PMID: 23082272
- PMCID: PMC3469081
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/143927
Successful treatment of long-term severe progressive interstitial pneumonia with low-dose corticosteroid and azathioprine in a patient with diffuse systemic sclerosis
Abstract
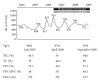
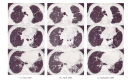
For progressive interstitial pneumonia (progressive IP) that accompanies diffuse systemic sclerosis (diffuse SSc), no treatment guidelines have yet been established, and it is a complication with a poor prognosis. We herein report a case in which combination therapy of a low-dose corticosteroid and low-dose azathioprine was performed for progressive SSc-IP in a 64-year-old female whose respiratory function was severely damaged for a long period of time and for whom improvement was achieved. The beneficial effect has continued for 3 years with no side effects being observed during the course.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis.Autoimmun Rev. 2011 Mar;10(5):248-55. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2010.09.012. Epub 2010 Sep 21. Autoimmun Rev. 2011. PMID: 20863911 Review.
-
Short-Term Lung Function Changes and Predictors of Progressive Systemic Sclerosis-Related Interstitial Lung Disease.Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul). 2020 Oct;83(4):312-320. doi: 10.4046/trd.2020.0043. Epub 2020 Jul 15. Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul). 2020. PMID: 32668825 Free PMC article.
-
Experience with azathioprine in systemic sclerosis associated with interstitial lung disease.Clin Rheumatol. 2004 Aug;23(4):306-9. doi: 10.1007/s10067-004-0906-7. Epub 2004 Apr 14. Clin Rheumatol. 2004. PMID: 15293090
-
Involvement of CD161+ Vδ1+ γδ T cells in systemic sclerosis: association with interstitial pneumonia.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2014 Dec;53(12):2259-69. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keu246. Epub 2014 Jun 27. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2014. PMID: 24972843
-
[Interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis].Rev Mal Respir. 2007 Oct;24(8):1035-46. doi: 10.1016/s0761-8425(07)92767-9. Rev Mal Respir. 2007. PMID: 18033190 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Interstitial Lung Disease in Systemic Sclerosis: Focus on Early Detection and Intervention.Open Access Rheumatol. 2019 Dec 9;11:283-307. doi: 10.2147/OARRR.S226695. eCollection 2019. Open Access Rheumatol. 2019. PMID: 31849543 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bérezné A, Valeyre D, Ranque B, Guillevin L, Mouthon L. Interstitial lung disease associated with systemic sclerosis: what is the evidence for efficacy of cyclophosphamide? Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 2007;1110:271–284. - PubMed
-
- Highland KB, Silver RM. Clinical aspects of lung involvement: lessons from idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and the scleroderma lung study. Current Rheumatology Reports. 2005;7(2):135–141. - PubMed
-
- Tashkin DP, Elashoff R, Clements PJ, et al. Cyclophosphamide versus placebo in scleroderma lung disease. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2006;354(25):2655–2666. - PubMed
-
- Khanna D, Furst DE, Clements PJ, Tashkin DP, Eckman MH. Oral cyclophosphamide for active scleroderma lung disease: a decision analysis. Medical Decision Making. 2008;28(6):926–937. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

