Inhibition of Akt Attenuates RPO-Induced Cardioprotection
- PMID: 23082275
- PMCID: PMC3469093
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/392457
Inhibition of Akt Attenuates RPO-Induced Cardioprotection
Abstract
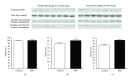
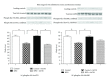
Previous studies have shown that red palm oil (RPO) supplementation protected rat hearts against ischaemia-reperfusion injury. Evidence from these studies suggested that Akt may be partly responsible for the observed protection. The aim of the current study was therefore to prove or refute the involvement of Akt in the RPO-induced cardioprotection by administration of a specific Akt inhibitor (A6730). Male Wistar rats were randomly divided into 2 groups: a control group receiving standard rat chow and an experimental group receiving standard rat chow plus 2 mL RPO for six weeks. Hearts were excised and mounted on the Langendorff perfusion system. Functional recovery was documented. A different set of hearts were freeze-clamped to assess total and phosphorylation status of Akt. Another set of hearts were subjected to the same perfusion conditions with addition of A6730. Hearts from this protocol were freeze-clamped and assessed for total and phospho-Akt. RPO improved functional recovery which was associated with increased phosphorylation of Akt on Ser473 and Thr308 residues. Blockade of Akt phosphorylation caused poor functional recovery. For the first time, these results prove that Akt plays an important role in the RPO-induced cardioprotection.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The effect of dietary red palm oil on the functional recovery of the ischaemic/reperfused isolated rat heart: the involvement of the PI3-kinase signaling pathway.Lipids Health Dis. 2009 May 29;8:18. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-8-18. Lipids Health Dis. 2009. PMID: 19480681 Free PMC article.
-
p38-MAPK and PKB/Akt, possible role players in red palm oil-induced protection of the isolated perfused rat heart?J Nutr Biochem. 2006 Apr;17(4):265-71. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2005.05.001. Epub 2005 May 31. J Nutr Biochem. 2006. PMID: 16229999
-
Dietary red palm oil supplementation reduces myocardial infarct size in an isolated perfused rat heart model.Lipids Health Dis. 2010 Jun 18;9:64. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-9-64. Lipids Health Dis. 2010. PMID: 20565865 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary red palm oil supplementation decreases infarct size in cholesterol fed rats.Lipids Health Dis. 2011 Jun 20;10:103. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-10-103. Lipids Health Dis. 2011. PMID: 21689423 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary red palm oil supplementation protects against the consequences of global ischemia in the isolated perfused rat heart.Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2005;14(4):340-7. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2005. PMID: 16326640
Cited by
-
Berbamine postconditioning protects the heart from ischemia/reperfusion injury through modulation of autophagy.Cell Death Dis. 2017 Feb 2;8(2):e2577. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.7. Cell Death Dis. 2017. PMID: 28151484 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Red Palm Oil on Myocardial Antioxidant Enzymes, Nitric Oxide Synthase and Heart Function in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Nov 21;18(11):2476. doi: 10.3390/ijms18112476. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29160855 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Hypercholesterolemia-Induced Oxidative/Nitrative Stress in the Heart.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:3863726. doi: 10.1155/2016/3863726. Epub 2015 Dec 14. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016. PMID: 26788247 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Callow AD. Cardiovascular disease 2005—the global picture. Vascular Pharmacology. 2006;45(5):302–307. - PubMed
-
- Brown AA, Hu FB. Dietary modulation of endothelial function: implications for cardiovascular disease. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2001;73(4):673–686. - PubMed
-
- Ceconi C, Boraso A, Cargnoni A, Ferrari R. Oxidative stress in cardiovascular disease: myth or fact? Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics. 2003;420(2):217–221. - PubMed
-
- Hertog MGL, Kromhout D, Aravanis C, et al. Flavonoid intake and long-term risk of coronary heart disease and cancer in the Seven Countries Study. Archives of Internal Medicine. 1995;155(4):381–386. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
