Phase-sensitive OCT imaging of multiple nanoparticle species using spectrally multiplexed single pulse photothermal excitation
- PMID: 23082297
- PMCID: PMC3470000
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.3.002579
Phase-sensitive OCT imaging of multiple nanoparticle species using spectrally multiplexed single pulse photothermal excitation
Abstract
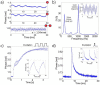
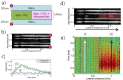
We apply phase-sensitive optical coherence tomography to image multiple nanoparticle species with two excitation wavelengths matched to their distinct absorption peaks. Using different modulation frequencies, multiple species collocated within the sample can be distinguished. In addition, we characterize single-pulse excitation schemes as a method to minimize bulk heating of the sample. We demonstrate this new scheme with B-mode photothermal measurements of tissue phantoms.
Keywords: (110.3000) Image quality assessment; (160.4236) Nanomaterials; (170.4500) Optical coherence tomography.
Figures


Similar articles
-
In vivo photothermal optical coherence tomography for non-invasive imaging of endogenous absorption agents.Biomed Opt Express. 2015 Apr 14;6(5):1707-25. doi: 10.1364/BOE.6.001707. eCollection 2015 May 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2015. PMID: 26137374 Free PMC article.
-
Photothermal detection of gold nanoparticles using phase-sensitive optical coherence tomography.Opt Express. 2008 Mar 31;16(7):4376-93. doi: 10.1364/oe.16.004376. Opt Express. 2008. PMID: 18542535
-
In vivo photothermal optical coherence tomography of gold nanorod contrast agents.Biomed Opt Express. 2012 Nov 1;3(11):2881-95. doi: 10.1364/BOE.3.002881. Epub 2012 Oct 17. Biomed Opt Express. 2012. PMID: 23162726 Free PMC article.
-
Mixed frequency-/time-domain coherent multidimensional spectroscopy: research tool or potential analytical method?Acc Chem Res. 2009 Sep 15;42(9):1310-21. doi: 10.1021/ar900032g. Acc Chem Res. 2009. PMID: 19445479
-
Multispectral nanoparticle contrast agents for true-color spectroscopic optical coherence tomography.Biomed Opt Express. 2012 Aug 1;3(8):1914-23. doi: 10.1364/BOE.3.001914. Epub 2012 Jul 20. Biomed Opt Express. 2012. PMID: 22876354 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A Review of Adaptive Optics Optical Coherence Tomography: Technical Advances, Scientific Applications, and the Future.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016 Jul 1;57(9):OCT51-68. doi: 10.1167/iovs.16-19103. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016. PMID: 27409507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative review of interferometric detection of plasmonic nanoparticles.Biomed Opt Express. 2013 Sep 16;4(10):2166-78. doi: 10.1364/BOE.4.002166. eCollection 2013. Biomed Opt Express. 2013. PMID: 24156072 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Izatt J. A., Kulkarni M. D., Wang H., Kobayashi K., Sivak M. V., “Optical Coherence Tomography and Microscopy in Gastrointestinal Tissues,” IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2(4), 1017–1028 (1996).10.1109/2944.577331 - DOI
-
- Kuranov R. V., Qiu J., McElroy A. B., Estrada A., Salvaggio A., Kiel J., Dunn A. K., Duong T. Q., Milner T. E., “Depth-resolved blood oxygen saturation measurement by dual-wavelength photothermal (DWP) optical coherence tomography,” Biomed. Opt. Express 2(3), 491–504 (2011).10.1364/BOE.2.000491 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
