Involvement of bacterial TonB-dependent signaling in the generation of an oligogalacturonide damage-associated molecular pattern from plant cell walls exposed to Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris pectate lyases
- PMID: 23082751
- PMCID: PMC3551730
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2180-12-239
Involvement of bacterial TonB-dependent signaling in the generation of an oligogalacturonide damage-associated molecular pattern from plant cell walls exposed to Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris pectate lyases
Abstract
Background: Efficient perception of attacking pathogens is essential for plants. Plant defense is evoked by molecules termed elicitors. Endogenous elicitors or damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) originate from plant materials upon injury or pathogen activity. While there are comparably well-characterized examples for DAMPs, often oligogalacturonides (OGAs), generated by the activity of fungal pathogens, endogenous elicitors evoked by bacterial pathogens have been rarely described. In particular, the signal perception and transduction processes involved in DAMP generation are poorly characterized.
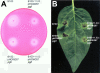
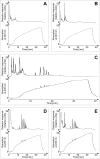
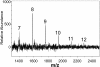
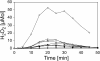
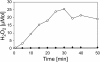
Results: A mutant strain of the phytopathogenic bacterium Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris deficient in exbD2, which encodes a component of its unusual elaborate TonB system, had impaired pectate lyase activity and caused no visible symptoms for defense on the non-host plant pepper (Capsicum annuum). A co-incubation of X. campestris pv. campestris with isolated cell wall material from C. annuum led to the release of compounds which induced an oxidative burst in cell suspension cultures of the non-host plant. Lipopolysaccharides and proteins were ruled out as elicitors by polymyxin B and heat treatment, respectively. After hydrolysis with trifluoroacetic acid and subsequent HPAE chromatography, the elicitor preparation contained galacturonic acid, the monosaccharide constituent of pectate. OGAs were isolated from this crude elicitor preparation by HPAEC and tested for their biological activity. While small OGAs were unable to induce an oxidative burst, the elicitor activity in cell suspension cultures of the non-host plants tobacco and pepper increased with the degree of polymerization (DP). Maximal elicitor activity was observed for DPs exceeding 8. In contrast to the X. campestris pv. campestris wild type B100, the exbD2 mutant was unable to generate elicitor activity from plant cell wall material or from pectin.
Conclusions: To our knowledge, this is the second report on a DAMP generated by bacterial features. The generation of the OGA elicitor is embedded in a complex exchange of signals within the framework of the plant-microbe interaction of C. annuum and X. campestris pv. campestris. The bacterial TonB-system is essential for the substrate-induced generation of extracellular pectate lyase activity. This is the first demonstration that a TonB-system is involved in bacterial trans-envelope signaling in the context of a pathogenic interaction with a plant.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The exbD2 gene as well as the iron-uptake genes tonB, exbB and exbD1 of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris are essential for the induction of a hypersensitive response on pepper (Capsicum annuum).Microbiology (Reading). 2000 May;146 ( Pt 5):1053-1060. doi: 10.1099/00221287-146-5-1053. Microbiology (Reading). 2000. PMID: 10832632
-
Molecular functions of Xanthomonas type III effector AvrBsT and its plant interactors in cell death and defense signaling.Planta. 2017 Feb;245(2):237-253. doi: 10.1007/s00425-016-2628-x. Epub 2016 Dec 7. Planta. 2017. PMID: 27928637 Review.
-
Regulation of cell wall-bound invertase in pepper leaves by Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria type three effectors.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e51763. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051763. Epub 2012 Dec 14. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23272161 Free PMC article.
-
The plant pathogen Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris exploits N-acetylglucosamine during infection.mBio. 2014 Sep 9;5(5):e01527-14. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01527-14. mBio. 2014. PMID: 25205095 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling role of oligogalacturonides derived during cell wall degradation.Plant Signal Behav. 2012 Nov;7(11):1447-9. doi: 10.4161/psb.21779. Epub 2012 Aug 23. Plant Signal Behav. 2012. PMID: 22918501 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pectin Induced Colony Expansion of Soil-Derived Flavobacterium Strains.Front Microbiol. 2021 Apr 6;12:651891. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.651891. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33889143 Free PMC article.
-
PECTIN ACETYLESTERASE9 Affects the Transcriptome and Metabolome and Delays Aphid Feeding.Plant Physiol. 2019 Dec;181(4):1704-1720. doi: 10.1104/pp.19.00635. Epub 2019 Sep 24. Plant Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31551361 Free PMC article.
-
A Meloidogyne graminicola Pectate Lyase Is Involved in Virulence and Activation of Host Defense Responses.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Mar 22;12:651627. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.651627. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 33868351 Free PMC article.
-
Independent Evolution with the Gene Flux Originating from Multiple Xanthomonas Species Explains Genomic Heterogeneity in Xanthomonas perforans.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019 Oct 1;85(20):e00885-19. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00885-19. Print 2019 Oct 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31375496 Free PMC article.
-
A pollen-specific calmodulin-binding protein, NPG1, interacts with putative pectate lyases.Sci Rep. 2014 Jun 12;4:5263. doi: 10.1038/srep05263. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 24919580 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

