A biofilm model developed to investigate survival and disinfection of Mycobacterium mucogenicum in potable water
- PMID: 23082863
- PMCID: PMC10840417
- DOI: 10.1080/08927014.2012.735231
A biofilm model developed to investigate survival and disinfection of Mycobacterium mucogenicum in potable water
Abstract
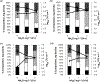
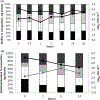
Water in healthcare environments can be a source for healthcare-associated infections (HAI). However, information on the exposure risk to opportunistic pathogens in potable water distribution systems (PWDS) is lacking. Laboratory studies characterizing the interaction of opportunistic pathogens with biofilms are needed to understand their role in water systems within healthcare facilities. A stable, repeatable, PWDS multi-species biofilm model comprising Sphingomonas paucimobilis, Methylobacterium sp., Delftia acidovorans, and Mycobacterium mucogenicum was developed in the CDC Biofilm Reactor (CBR), reaching 6 log(10) CFU cm(-2) within 6 days. The model was used to investigate the interaction of the opportunistic pathogen M. mucogenicum with the other species, and to determine the efficacy of monochloramine (NH(2)Cl) as a disinfectant against 2-week-old biofilms. Addition of 1 or 2 mg l(-1) NH(2)Cl resulted in the same or an increased log density of viable M. mucogenicum in the biofilm while inactivating some of the Proteobacteria. Although M. mucogenicum preferentially resided in the biofilm, NH(2)Cl exposure caused release of viable M. mucogenicum from the biofilm into the water. Additional studies with this model should determine if sodium hypochlorite has a comparative effect and if other nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) respond to NH(2)Cl similarly.
Figures


References
-
- Anaissie EJ, Penzak SR, Dignani MC. 2002. The hospital water supply as a source of nosocomial infections: a plea for action. Arch Int Med 162:1483–1492. - PubMed
-
- APHA AWWA, WEF. 2005. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. 21st ed. Washington (DC: ): American Public Health Association. p. 4–56 to 4–76.
-
- Berry D, Xi C, Raskin L. 2006. Microbial ecology of drinking water distribution systems. Curr Opin Biotech 17:297–302. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
