The effect of alpha-v integrin inhibition on the malignant characteristics of medulloblastoma
- PMID: 23082872
- PMCID: PMC3709582
- DOI: 10.3171/2012.9.PEDS12268
The effect of alpha-v integrin inhibition on the malignant characteristics of medulloblastoma
Abstract
Object: Hypoxia induces an aggressive phenotype in some brain tumors in part due to hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) and integrin expression. The importance of hypoxia in medulloblastoma is unclear and the interaction of HIF-1α and c-Myc in medulloblastoma has not been explored. The objective of this study was to determine if hypoxia induces an aggressive phenotype in human medulloblastoma cells that constitutively express high (D283 Med) or low (DAOY) levels of c-Myc and to determine if blocking α(v) integrins with the monoclonal antibody intetumumab inhibits hypoxia-induced cellular stress responses.
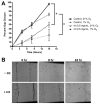
Methods: Cells were grown at 21% and 1% O(2) and in the presence or absence of intetumumab. Measures of malignancy evaluated included cell proliferation, cell migration, and expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), α(v) integrins, HIF-1α, and c-Myc.
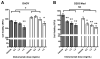
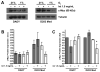
Results: Both cell lines robustly expressed α(v) integrins. Hypoxic DAOY cells showed significantly increased proliferation compared with normoxic controls (p < 0.05), whereas D283 Med cells did not. Both cell lines exhibited a dose-dependent decrease in proliferation when treated with intetumumab (p < 0.05). Hypoxia did not increase DAOY migration, but intetumumab significantly inhibited migration at both oxygen conditions (p < 0.05). Intetumumab significantly decreased VEGF levels in DAOY cells at both oxygen conditions (p < 0.05) and in normoxic D283 cells (p < 0.01). Neither cell line demonstrated increased HIF-1α expression in response to hypoxia. However, hypoxic D283 Med cells grown in the presence of intetumumab demonstrated significantly decreased c-Myc expression (p < 0.05).
Conclusions: Hypoxia did not clearly induce a more aggressive phenotype in medulloblastoma cells. Despite this result, intetumumab decreased medulloblastoma cell proliferation and migration and variably decreased VEGF and c-Myc expression in hypoxic conditions. Targeting α(v) integrins represents a promising potential adjuvant modality in the treatment of medulloblastoma, particularly subtypes that metastasize and overexpress VEGF and c-Myc.
Figures


References
-
- Brat DJ, Castellano-Sanchez AA, Hunter SB, Pecot M, Cohen C, Hammond EH, et al. Pseudopalisades in glioblastoma are hypoxic, express extracellular matrix proteases, and are formed by an actively migrating cell population. Cancer Res. 2004;64:920–927. - PubMed
-
- Chu FM, Picus J, Fracasso PM, Dreicer R, Lang Z, Foster B. A phase 1, multicenter, open-label study of the safety of two dose levels of a human monoclonal antibody to human alpha(v) integrins, intetumumab, in combination with docetaxel and prednisone in patients with castrate-resistant metastatic prostate cancer. Invest New Drugs. 2011;29:674–679. - PubMed
-
- Friedlander M, Brooks PC, Shaffer RW, Kincaid CM, Varner JA, Cheresh DA. Definition of two angiogenic pathways by distinct alpha v integrins. Science. 1995;270:1500–1502. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

