Analysis of posaconazole as oral antifungal prophylaxis in pediatric patients under 12 years of age following allogeneic stem cell transplantation
- PMID: 23082876
- PMCID: PMC3514296
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2334-12-263
Analysis of posaconazole as oral antifungal prophylaxis in pediatric patients under 12 years of age following allogeneic stem cell transplantation
Abstract
Background: Pediatric patients undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) are at high risk of acquiring fungal infections. Antifungal prophylaxis shortly after transplantation is therefore indicated, but data for pediatric patients under 12 years of age are scarce. To address this issue, we retrospectively assessed the safety, feasibility, and initial efficacy of prophylactic posaconazole in children.
Methods: 60 consecutive pediatric patients with a median age of 6.0 years who underwent allogeneic HSCT between August 2007 and July 2010 received antifungal prophylaxis with posaconazole in the outpatient setting. 28 pediatric patients received an oral suspension at 5 mg/kg body weight b.i.d., and 32 pediatric patients received the suspension at 4 mg/kg body weight t.i.d. The observation period lasted from start of treatment with posaconazole until its termination (maximum of 200 days post-transplant).
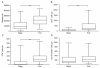
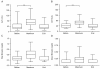
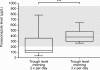
Results: Pediatric patients who received posaconazole at 4 mg/kg body weight t.i.d. had a median trough level of 383 μg/L. Patients who received posaconazole at 5 mg/kg body weight b.i.d. had a median trough level of 134 μg/L. Both regimens were well tolerated without severe side effects. In addition, no proven or probable invasive mycosis was observed.
Conclusion: Posaconazole was a well-tolerated, safe, and effective oral antifungal prophylaxis in pediatric patients who underwent high-dose chemotherapy and HSCT. Posaconazole at a dosage of 12 mg/kg body weight divided in three doses produced consistently higher morning trough levels than in patients who received posaconazole 5 mg/kg body weight b.i.d. Larger prospective trials are needed to obtain reliable guidelines for antifungal prophylaxis in children after HSCT.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy, safety and feasibility of antifungal prophylaxis with posaconazole tablet in paediatric patients after haematopoietic stem cell transplantation.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2017 Jul;143(7):1281-1292. doi: 10.1007/s00432-017-2369-7. Epub 2017 Mar 3. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28258343 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Antifungal prophylaxis with posaconazole vs. fluconazole or itraconazole in pediatric patients with neutropenia.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2015 Jun;34(6):1189-200. doi: 10.1007/s10096-015-2340-y. Epub 2015 Feb 14. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 25680318 Free PMC article.
-
Caspofungin as antifungal prophylaxis in pediatric patients undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a retrospective analysis.BMC Infect Dis. 2012 Jul 2;12:151. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-12-151. BMC Infect Dis. 2012. PMID: 22747637 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Posaconazole in immunocompromised pediatric patients.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2018 Jul;16(7):543-553. doi: 10.1080/14787210.2018.1490177. Epub 2018 Jul 3. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2018. PMID: 29912581 Review.
-
Comparison of Antifungal Prophylaxis Drugs in Patients With Hematological Disease or Undergoing Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis.JAMA Netw Open. 2020 Oct 1;3(10):e2017652. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.17652. JAMA Netw Open. 2020. PMID: 33030550 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Potency and Preclinical Evidence of Synergy of Oral Azole Drugs and Miltefosine in an Ex Vivo Model of Leishmania (Viannia) panamensis Infection.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2022 Jan 18;66(1):e0142521. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01425-21. Epub 2021 Oct 25. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2022. PMID: 34694879 Free PMC article.
-
Retrospective Analysis of Posaconazole Suspension Dosing Strategies in a Pediatric Oncology Population: Single-Center Experience.J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2017 Sep 1;6(3):e149-e151. doi: 10.1093/jpids/pix058. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2017. PMID: 28903522 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy, safety and feasibility of antifungal prophylaxis with posaconazole tablet in paediatric patients after haematopoietic stem cell transplantation.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2017 Jul;143(7):1281-1292. doi: 10.1007/s00432-017-2369-7. Epub 2017 Mar 3. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28258343 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Invasive Aspergillosis in Children: Update on Current Guidelines.Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2018 Sep 1;10(1):e2018048. doi: 10.4084/MJHID.2018.048. eCollection 2018. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 30210741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antifungal Prophylaxis With Posaconazole in Immunocompromised Children Younger Than 13 Years.J Pediatr Pharmacol Ther. 2022;27(1):57-62. doi: 10.5863/1551-6776-27.1.57. Epub 2021 Dec 22. J Pediatr Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 35002560 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Walsh TJ, Raad I, Patterson TF, Chandrasekar P, Donowitz GR, Graybill R, Greene RE, Hachem R, Hadley S, Herbrecht R, Langston A, Louie A, Ribaud P, Segal BH, Stevens DA, van Burik JA, White CS, Corcoran G, Gogate J, Krishna G, Pedicone L, Hardalo C, Perfect JR. Treatment of invasive aspergillosis with posaconazole in patients who are refractory to or intolerant of conventional therapy: an externally controlled trial. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;44:2–12. doi: 10.1086/508774. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

