Lessons from Anaplasma phagocytophilum: chromatin remodeling by bacterial effectors
- PMID: 23082961
- PMCID: PMC3664514
- DOI: 10.2174/187152612804142242
Lessons from Anaplasma phagocytophilum: chromatin remodeling by bacterial effectors
Abstract
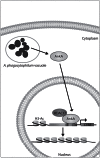
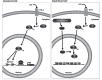
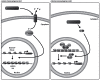
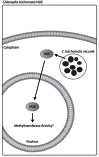
Bacterial pathogens can alter global host gene expression via histone modifications and chromatin remodeling in order to subvert host responses, including those involved with innate immunity, allowing for bacterial survival. Shigella flexneri, Listeria monocytogenes, Chlamydia trachomatis, and Anaplasma phagocytophilum express effector proteins that modify host histones and chromatin structure. A. phagocytophilum modulates granulocyte respiratory burst in part by dampening transcription of several key phagocyte oxidase genes. The A. phagocytophilum protein AnkA localizes to the myeloid cell nucleus where it binds AT-rich regions in the CYBB promoter and decreases its transcription. AT-rich regions of DNA are characteristic of matrix attachment regions (MARs) which are critical for chromatin structure and transcription. MAR-binding proteins, such as SATB1, interact with histone modifying enzymes resulting in altered gene expression. With A. phagocytophilum infection, histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) expression is increased and histone H3 acetylation is decreased at the CYBB promoter, suggesting a role for AnkA in altering host epigenetics and modulating gene transcription, at this, and perhaps other loci. This review will focus on how bacterial pathogens alter host epigenetics, by specifically examining A. phagocytophilum AnkA cis-regulation of CYBB transcription and epigenetic changes associated with infection.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chromatin-bound bacterial effector ankyrin A recruits histone deacetylase 1 and modifies host gene expression.Cell Microbiol. 2015 Nov;17(11):1640-52. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12461. Epub 2015 Jun 11. Cell Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25996657 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing of host cell CYBB gene expression by the nuclear effector AnkA of the intracellular pathogen Anaplasma phagocytophilum.Infect Immun. 2009 Jun;77(6):2385-91. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00023-09. Epub 2009 Mar 23. Infect Immun. 2009. PMID: 19307214 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Anaplasma phagocytophilum AnkA-DNA Interactions Are Enriched in Intergenic Regions and Gene Promoters and Correlate with Infection-Induced Differential Gene Expression.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016 Sep 20;6:97. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2016.00097. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27703927 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of evasion of neutrophil killing by Anaplasma phagocytophilum.Curr Opin Hematol. 2006 Jan;13(1):28-33. doi: 10.1097/01.moh.0000190109.00532.56. Curr Opin Hematol. 2006. PMID: 16319684 Review.
-
Effector bottleneck: microbial reprogramming of parasitized host cell transcription by epigenetic remodeling of chromatin structure.Front Genet. 2014 Aug 14;5:274. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00274. eCollection 2014. Front Genet. 2014. PMID: 25177343 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Moonlighting in Rickettsiales: Expanding Virulence Landscape.Trop Med Infect Dis. 2022 Feb 19;7(2):32. doi: 10.3390/tropicalmed7020032. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35202227 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioinformatic and mass spectrometry identification of Anaplasma phagocytophilum proteins translocated into host cell nuclei.Front Microbiol. 2015 Feb 6;6:55. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00055. eCollection 2015. Front Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25705208 Free PMC article.
-
From Gene to Protein-How Bacterial Virulence Factors Manipulate Host Gene Expression During Infection.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 25;21(10):3730. doi: 10.3390/ijms21103730. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32466312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Akirin/Subolesin regulatory mechanisms at host/tick-pathogen interactions.Microlife. 2021 Nov 11;3:uqab012. doi: 10.1093/femsml/uqab012. eCollection 2022. Microlife. 2021. PMID: 37223345 Free PMC article.
-
NF-κBp50 and HDAC1 Interaction Is Implicated in the Host Tolerance to Infection Mediated by the Bacterial Quorum Sensing Signal 2-Aminoacetophenone.Front Microbiol. 2017 Jun 30;8:1211. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01211. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28713342 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bhavsar A P, Guttman J A, Finlay B B. Manipulation of host-cell pathways by bacterial pathogens. Nature. 2007;449:827–834. - PubMed
-
- Bryant P A, Venter D, Robins-Browne R, Curtis N. Chips with everything: DNA microarrays in infectious diseases. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2004;4:100–111. - PubMed
-
- Clayton A L, Mahadevan L C. MAP kinase-mediated phosphoacetylation of histone H3 and inducible gene regulation. FEBS Lett. 2003;546:51–58. - PubMed
-
- Mahadevan L C, Willis A C, Barratt M J. Rapid histone H3 phosphorylation in response to growth factors, phorbol esters, okadaic acid, and protein synthesis inhibitors. Cell. 1991;65:775–783. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

