(E)-2,4-bis(p-hydroxyphenyl)-2-butenal has an antiproliferative effect on NSCLC cells induced by p38 MAPK-mediated suppression of NF-κB and up-regulation of TNFRSF10B (DR5)
- PMID: 23082969
- PMCID: PMC3596651
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.12024
(E)-2,4-bis(p-hydroxyphenyl)-2-butenal has an antiproliferative effect on NSCLC cells induced by p38 MAPK-mediated suppression of NF-κB and up-regulation of TNFRSF10B (DR5)
Abstract
Background and purpose: The Maillard Reaction Products (MRPs) are known to be effective in chemoprevention. Here we focused on the anticancer effects of (E)-2,4-bis(p-hydroxyphenyl)-2-butenal (a MRP) on human non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells and its mechanism of action.
Experimental approach: We analysed the activity of (E)-2,4-bis(p-hydroxyphenyl)-2-butenal on NSCLC cells (NCI-H460 and A549) by use of Western blot analysis for major apoptotic proteins, MAPK, NF-κB and death receptor expression. We also used RT-PCR to determine its effects on death receptor mRNA expression, EMSA for effects on NF-κB DNA binding activity and colony formation assay for effects of inhibitors on (E)-2,4-bis(p-hydroxyphenyl)-2-butenal's actions.
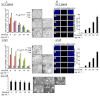
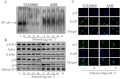
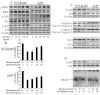
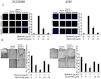
Key results: (E)-2,4-bis(p-hydroxyphenyl)-2-butenal induced a concentration (10-40 μg·mL⁻¹)- and time (30 min-72 h)-dependent inhibitory effect on the growth of NSCLC cells due to induction of apoptosis. Concomitantly, it significantly increased the expression of apoptotic proteins such as cleaved caspase-3, cleaved caspase-9, Bax and p53, but down-regulated the expression of anti-apoptotic proteins Bcl-2, cIAP1 and cIAP2. This effect was induced by up-regulation of MAPK and death receptor proteins TNFRSF12, TNFRSF10B and TNFRSF21, but suppression of NF-κB. Of the death receptors activated, only TNFRSF10B knock down with siRNA reversed the effect of (E)-2,4-bis(p-hydroxyphenyl)-2-butenal. Even though all the MAPKs were activated, only pretreatment with a p38 MAPK inhibitor reversed (E)-2,4-bis(p-hydroxyphenyl)-2-butenal-induced cell growth inhibition, increase in cleaved caspase-3, -9 and TNFRSF10B expression, and NF-κB inactivation.
Conclusions and implications: (E)-2,4-bis(p-hydroxyphenyl)-2-butenal induces apoptosis in NSCLC cells by p38 MAPK-mediated suppression of NF-κB and activation of TNFRSF10B, which then activates the caspase-3 and caspase-9 pathways.
© 2012 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2012 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures

Similar articles
-
(E)-2,4-Bis(p-hydroxyphenyl)-2-butenal inhibits tumor growth via suppression of NF-κB and induction of death receptor 6.Apoptosis. 2014 Jan;19(1):165-78. doi: 10.1007/s10495-013-0903-x. Apoptosis. 2014. PMID: 24052407
-
(E)-2,4-Bis(p-hydroxyphenyl)-2-butenal enhanced TRAIL-induced apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells through downregulation of NF-κB/STAT3 pathway.Arch Pharm Res. 2014 May;37(5):652-61. doi: 10.1007/s12272-013-0326-9. Epub 2014 Jan 4. Arch Pharm Res. 2014. PMID: 24390815
-
Anti-arthritis effects of (E)-2,4-bis(p-hydroxyphenyl)-2-butenal are mediated by inhibition of the STAT3 pathway.Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Jun;171(11):2900-12. doi: 10.1111/bph.12619. Br J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24520814 Free PMC article.
-
NF-κB in the crosshairs: Rethinking an old riddle.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2018 Feb;95:108-112. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2017.12.020. Epub 2017 Dec 23. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29277662 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Caspase-8 as a therapeutic target in cancer.Cancer Lett. 2013 May 28;332(2):133-40. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2010.07.022. Epub 2010 Sep 3. Cancer Lett. 2013. PMID: 20817393 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Luteolin exerts an anticancer effect on NCI-H460 human non-small cell lung cancer cells through the induction of Sirt1-mediated apoptosis.Mol Med Rep. 2015 Sep;12(3):4196-4202. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3956. Epub 2015 Jun 18. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 26096576 Free PMC article.
-
Piperlongumine inhibits lung tumor growth via inhibition of nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathway.Sci Rep. 2016 May 20;6:26357. doi: 10.1038/srep26357. Sci Rep. 2016. Retraction in: Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 30;15(1):15188. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-99020-w. PMID: 27198178 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Anticancer effect of tectochrysin in colon cancer cell via suppression of NF-kappaB activity and enhancement of death receptor expression.Mol Cancer. 2015 Jun 30;14:124. doi: 10.1186/s12943-015-0377-2. Mol Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26123287 Free PMC article.
-
Novel synthetic (E)-2-methoxy-4-(3-(4-methoxyphenyl) prop-1-en-1-yl) phenol inhibits arthritis by targeting signal transducer and activator of transcription 3.Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 15;6:36852. doi: 10.1038/srep36852. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27845373 Free PMC article.
-
A small molecule, (E)-2-methoxy-4-(3-(4-methoxyphenyl) prop-1-en-1-yl) phenol suppresses tumor growth via inhibition of IkappaB kinase β in colorectal cancer in vivo and in vitro.Oncotarget. 2017 Aug 24;8(53):91258-91269. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20440. eCollection 2017 Oct 31. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29207641 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashkenazi A. Targeting death and decoy receptors of the tumor-necrosis factor super family. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:420–430. - PubMed
-
- Atrooz OM. The effects of Maillard reaction products on apple and potato polyphenoloxidase and their antioxidant activity. Int J Food Sci Technol. 2008;43:490–494.
-
- Baud V, Karin M. Signal transduction by tumor necrosis factor and its relatives. Trends Cell Biol. 2001;11:372–377. - PubMed
-
- Bian J, Wang K, Kong X, Liu H, Chen F, Hu M, et al. Caspase- and p38-MAPK-dependent induction of apoptosis in A549 lung cancer cells by Newcastle disease virus. Arch Virol. 2011;156:1335–1344. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

