Exogenous basic fibroblast growth factor inhibits ER stress-induced apoptosis and improves recovery from spinal cord injury
- PMID: 23082997
- PMCID: PMC6493620
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.12013
Exogenous basic fibroblast growth factor inhibits ER stress-induced apoptosis and improves recovery from spinal cord injury
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the mechanism of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-induced apoptosis as well as the protective action of basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) both in vivo and in vitro.
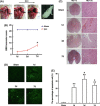
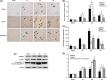
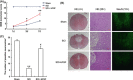
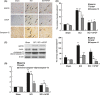
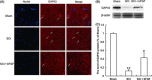
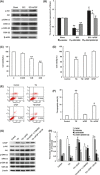
Methods and results: ER stress-induced apoptosis was involved in the injuries of spinal cord injury (SCI) model rat. bFGF administration improved the recovery and increased the survival of neurons in spinal cord lesions in model rat. The protective effect of bFGF is related to the inhibition of CHOP, GRP78 and caspase-12, which are ER stress-induced apoptosis response proteins. bFGF administration also increased the survival of neurons and the expression of growth-associated protein 43 (GAP43), which is related to neural regeneration. The protective effect of bFGF is related to the activation of downstream signals, PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β and ERK1/2, especially in the ER stress cell model.
Conclusions: This is the first study to illustrate that the role of bFGF in SCI recovery is related to the inhibition of ER stress-induced cell death via the activation of downstream signals. Our work also suggested a new trend for bFGF drug development in central neural system injuries, which are involved in chronic ER stress-induced apoptosis.
© 2012 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Penas C, Guzman MS, Verdu E, et al. Spinal cord injury induces endoplasmic reticulum stress with different cell‐type dependent response. J Neurochem 2007;102:1242–1255. - PubMed
-
- Dasari VR, Veeravalli KK, Tsung AJ, et al. Neuronal apoptosis is inhibited by cord blood stem cells after spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma 2009;26:2057–2069. - PubMed
-
- Beattie MS. Inflammation and apoptosis: linked therapeutic targets in spinal cord injury. Trends Mol Med 2004;10:580–583. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

