Pharmacological characterization of LPS and opioid interactions at the toll-like receptor 4
- PMID: 23083095
- PMCID: PMC3596647
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.12028
Pharmacological characterization of LPS and opioid interactions at the toll-like receptor 4
Abstract
Background and purpose: Previous work in our laboratory showed opioid agents inhibit cytokine expression in astrocytes. Recently, Watkins and colleagues hypothesized that opioid agonists activate toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) signalling, which leads to neuroinflammation. To test this hypothesis, we characterized LPS and opioid effects on TLR4 signalling in reporter cells.
Experimental approach: NF-κB reporter cells expressing high levels of TLR4 were used to compare LPS and opioid effects on NF-κB activation, a pathway activated by TLR4 stimulation.
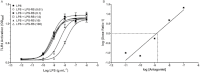
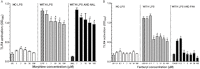
Key results: LPS increased TLR4 signalling in a concentration-dependent manner and was antagonized by LPS antagonist (LPS-RS, from Rhodobacter sphaeroides). A concentration ratio analysis showed that LPS-RS was a competitive antagonist. The opioid agonists, morphine and fentanyl, produced minor activation of TLR4 signalling when given alone. When tested following LPS stimulation, opioid agonists inhibited NF-κB activation but this inhibition was not blocked by the general opioid antagonist, naloxone, nor by the selective μ opioid receptor antagonist, β-FNA. Indeed, both naloxone and β-FNA also inhibited NF-κB activation in reporter cells. Further examination of fentanyl and β-FNA effects revealed that both opioid agents inhibited LPS signalling in a non-competitive fashion.
Conclusions and implications: These results show that LPS-RS is a competitive antagonist at the TLR4 complex, and that both opioid agonists and antagonists inhibit LPS signalling in a non-competitive fashion through a non-GPCR, opioid site(s) in the TLR4 signalling pathway. If confirmed, existing opioid agents or other drug molecules more selective at this novel site may provide a new therapeutic approach to the treatment of neuroinflammation.
© 2012 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2012 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
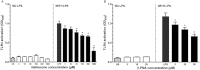

References
-
- Börner C, Stumm R, Höllt V, Kraus J. Comparative analysis of mu-opioid receptor expression in immune and neuronal cells. J Neuroimmunol. 2007;188:56–63. - PubMed
-
- Börner C, Höllt V, Kraus J. Mechanisms of the inhibition of nuclear factor-κB by morphine in neuronal cells. Mol Pharmacol. 2012;81:587–597. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

