Could titanium oxide coating from a sol-gel process make stone baskets more resistant to laser radiation at 2.1 μm?
- PMID: 23083224
- PMCID: PMC3599394
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-5751-11-15
Could titanium oxide coating from a sol-gel process make stone baskets more resistant to laser radiation at 2.1 μm?
Abstract
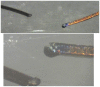
Background: Stone baskets could be easily destroyed by Holmium:YAG-laser at an endourologic treatment, with respect to this, we try to improve the resistance by coating them with a titanium oxide layer. The layer was established by a sol-gel-process.
Materials and methods: Six new baskets (Equadus, Opi Med, Ettlingen, Germany) were used: 1.8 Ch. with 4 wires (diameter 0.127 mm). Three baskets were coated with a layer of titanium oxide established by a sol-gel process at the BioCerEntwicklungs GmbH in Bayreuth (~100 nanometres thickness). The lithotripter was a Holmium:YAG laser (Auriga XL, Starmedtec, Starnberg, Germany). 10 uncoated and 10 coated wires were tested with 610 mJ (the minimal clinical setting) and 2 uncoated and 2 coated wires were tested with 110 mJ. The wires were locked in a special holding instrument under water and the laser incident angle was 90°. The endpoint was gross visible damage to the wire and loss of electric conduction.
Results: Only two coated wires resisted two pulses (one in the 610 mJ and one in the 110 mJ setting). All other wires were destroyed after one pulse.
Conclusion: This was the first attempt at making stone baskets more resistant to a Holmium:YAG laser beam. Titanium oxide deposited by a sol-gel-process on a titanium-nickel alloy did not result in better resistance to laser injuries.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Risk of collateral damage to endourologic tools by holmium:YAG laser energy.J Endourol. 2006 Jul;20(7):495-7. doi: 10.1089/end.2006.20.495. J Endourol. 2006. PMID: 16859463
-
Impact of collateral damage to endourologic tools during laser lithotripsy--in vitro comparison of three different clinical laser systems.J Endourol. 2011 Apr;25(4):667-72. doi: 10.1089/end.2010.0169. Epub 2011 Mar 7. J Endourol. 2011. PMID: 21381958
-
[The experimental study on sol-gel technique of coating titanium].Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2004 Jul;39(4):306-8. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2004. PMID: 15454016 Chinese.
-
Thulium fiber laser: the new player for kidney stone treatment? A comparison with Holmium:YAG laser.World J Urol. 2020 Aug;38(8):1883-1894. doi: 10.1007/s00345-019-02654-5. Epub 2019 Feb 6. World J Urol. 2020. PMID: 30729311 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lasers for stone treatment: how safe are they?Curr Opin Urol. 2020 Mar;30(2):130-134. doi: 10.1097/MOU.0000000000000706. Curr Opin Urol. 2020. PMID: 31895074 Review.
References
-
- Hesse A, Brändle E, Wilbert D, Köhrmann K-U, Alken P. Study on the prevalence and incidence of urolithiasis in Germany comparing the years 1979 vs. 2000. EurUrol. 2003;44:709–713. - PubMed
-
- Müller SC, Hofmann R, Köhrmann K-U, Hesse A. Epidemiologie, instrumentelle Therapie und Metaphylaxe des Harnsteinleidens. DtschArztebl. 2004;101:A1331–A1336.
-
- Smith AD, Baldlani G, Bagley D, v. Clayman R, Docimo SG, Jordan GH, Kavoussi LR, Lee BR, Lingeman JE, Preminger GM, Segura JW. Textbook of Endourology. second. Canada: BC Decker; 2007.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

