CLC anion channel regulatory phosphorylation and conserved signal transduction domains
- PMID: 23083714
- PMCID: PMC3475328
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2012.09.001
CLC anion channel regulatory phosphorylation and conserved signal transduction domains
Abstract
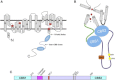
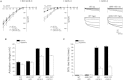
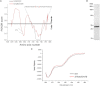
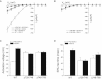
The signaling mechanisms that regulate CLC anion channels are poorly understood. Caenorhabditis elegans CLH-3b is a member of the CLC-1/2/Ka/Kb channel subfamily. CLH-3b is activated by meiotic cell-cycle progression and cell swelling. Inhibition is brought about by GCK-3 kinase-mediated phosphorylation of S742 and S747 located on a ∼176 amino acid disordered domain linking CBS1 and CBS2. Much of the inter-CBS linker is dispensable for channel regulation. However, deletion of a 14 amino acid activation domain encompassing S742 and S747 inhibits channel activity to the same extent as GCK-3. The crystal structure of CmCLC demonstrated that CBS2 interfaces extensively with an intracellular loop connecting membrane helices H and I, the C-terminus of helix D, and a short linker connecting helix R to CBS1. Point mutagenesis of this interface identified two highly conserved aromatic amino acid residues located in the H-I loop and the first α-helix (α1) of CBS2. Mutation of either residue to alanine rendered CLH-3b insensitive to GCK-3 inhibition. We suggest that the dephosphorylated activation domain normally interacts with CBS1 and/or CBS2, and that conformational information associated with this interaction is transduced through a conserved signal transduction module comprising the H-I loop and CBS2 α1.
Copyright © 2012 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Regulatory Conformational Coupling between CLC Anion Channel Membrane and Cytoplasmic Domains.Biophys J. 2016 Nov 1;111(9):1887-1896. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2016.09.037. Biophys J. 2016. PMID: 27806270 Free PMC article.
-
Role of CBS and Bateman Domains in Phosphorylation-Dependent Regulation of a CLC Anion Channel.Biophys J. 2016 Nov 1;111(9):1876-1886. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2016.09.036. Biophys J. 2016. PMID: 27806269 Free PMC article.
-
Differential regulation of a CLC anion channel by SPAK kinase ortholog-mediated multisite phosphorylation.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2012 Jun 15;302(12):C1702-12. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00419.2011. Epub 2012 Feb 22. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22357738 Free PMC article.
-
CBS domains: structure, function, and pathology in human proteins.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2005 Dec;289(6):C1369-78. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00282.2005. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2005. PMID: 16275737 Review.
-
CLC chloride channels: correlating structure with function.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2002 Aug;12(4):531-9. doi: 10.1016/s0959-440x(02)00358-5. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2002. PMID: 12163078 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulatory Conformational Coupling between CLC Anion Channel Membrane and Cytoplasmic Domains.Biophys J. 2016 Nov 1;111(9):1887-1896. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2016.09.037. Biophys J. 2016. PMID: 27806270 Free PMC article.
-
Role of CBS and Bateman Domains in Phosphorylation-Dependent Regulation of a CLC Anion Channel.Biophys J. 2016 Nov 1;111(9):1876-1886. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2016.09.036. Biophys J. 2016. PMID: 27806269 Free PMC article.
-
Novel exc Genes Involved in Formation of the Tubular Excretory Canals of Caenorhabditis elegans.G3 (Bethesda). 2019 May 7;9(5):1339-1353. doi: 10.1534/g3.119.200626. G3 (Bethesda). 2019. PMID: 30885922 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of the ClC chloride channel CLH-1 in food-associated salt chemotaxis behavior of C. elegans.Elife. 2021 Jan 25;10:e55701. doi: 10.7554/eLife.55701. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33492228 Free PMC article.
-
WNK Kinases in Development and Disease.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2017;123:1-47. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2016.08.004. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 28236964 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jentsch T.J. CLC chloride channels and transporters: from genes to protein structure, pathology and physiology. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008;43:3–36. - PubMed
-
- Dutzler R., Campbell E.B., MacKinnon R. Gating the selectivity filter in ClC chloride channels. Science. 2003;300:108–112. - PubMed
-
- Dutzler R., Campbell E.B., MacKinnon R. X-ray structure of a ClC chloride channel at 3.0 A reveals the molecular basis of anion selectivity. Nature. 2002;415:287–294. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

