Imaging neural activity using Thy1-GCaMP transgenic mice
- PMID: 23083733
- PMCID: PMC4059513
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.07.011
Imaging neural activity using Thy1-GCaMP transgenic mice
Abstract
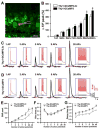
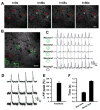
The ability to chronically monitor neuronal activity in the living brain is essential for understanding the organization and function of the nervous system. The genetically encoded green fluorescent protein-based calcium sensor GCaMP provides a powerful tool for detecting calcium transients in neuronal somata, processes, and synapses that are triggered by neuronal activities. Here we report the generation and characterization of transgenic mice that express improved GCaMPs in various neuronal subpopulations under the control of the Thy1 promoter. In vitro and in vivo studies show that calcium transients induced by spontaneous and stimulus-evoked neuronal activities can be readily detected at the level of individual cells and synapses in acute brain slices, as well as chronically in awake, behaving animals. These GCaMP transgenic mice allow investigation of activity patterns in defined neuronal populations in the living brain and will greatly facilitate dissecting complex structural and functional relationships of neural networks.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures





References
-
- Bozza T, McGann JP, Mombaerts P, Wachowiak M. In vivo imaging of neuronal activity by targeted expression of a genetically encoded probe in the mouse. Neuron. 2004;42:9–21. - PubMed
-
- Chen X, Leischner U, Rochefort NL, Nelken I, Konnerth A. Functional mapping of single spines in cortical neurons in vivo. Nature. 2011;475:501–505. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

