Genetic removal of p70 S6 kinase 1 corrects molecular, synaptic, and behavioral phenotypes in fragile X syndrome mice
- PMID: 23083736
- PMCID: PMC3479445
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.07.022
Genetic removal of p70 S6 kinase 1 corrects molecular, synaptic, and behavioral phenotypes in fragile X syndrome mice
Abstract
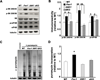
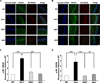
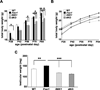
Fragile X syndrome (FXS) is the leading inherited cause of autism and intellectual disability. Aberrant synaptic translation has been implicated in the etiology of FXS, but most lines of research on therapeutic strategies have targeted protein synthesis indirectly, far upstream of the translation machinery. We sought to perturb p70 ribosomal S6 kinase 1 (S6K1), a key translation initiation and elongation regulator, in FXS model mice. We found that genetic reduction of S6K1 prevented elevated phosphorylation of translational control molecules, exaggerated protein synthesis, enhanced mGluR-dependent long-term depression (LTD), weight gain, and macro-orchidism in FXS model mice. In addition, S6K1 deletion prevented immature dendritic spine morphology and multiple behavioral phenotypes, including social interaction deficits, impaired novel object recognition, and behavioral inflexibility. Our results support the model that dysregulated protein synthesis is the key causal factor in FXS and that restoration of normal translation can stabilize peripheral and neurological function in FXS.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



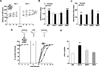

References
-
- Bear MF, Huber KM, Warren ST. The mGluR theory of fragile X mental retardation. Trends Neurosci. 2004;27:370–377. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

