Central venous pressure and shock index predict lack of hemodynamic response to volume expansion in septic shock: a prospective, observational study
- PMID: 23084132
- PMCID: PMC3621131
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2012.07.021
Central venous pressure and shock index predict lack of hemodynamic response to volume expansion in septic shock: a prospective, observational study
Abstract
Purpose: Volume expansion is a common therapeutic intervention in septic shock, although patient response to the intervention is difficult to predict. Central venous pressure (CVP) and shock index have been used independently to guide volume expansion, although their use is questionable. We hypothesize that a combination of these measurements will be useful.
Methods: In a prospective, observational study, patients with early septic shock received 10-mL/kg volume expansion at their treating physician's discretion after brief initial resuscitation in the emergency department. Central venous pressure and shock index were measured before volume expansion interventions. Cardiac index was measured immediately before and after the volume expansion using transthoracic echocardiography. Hemodynamic response was defined as an increase in a cardiac index of 15% or greater.
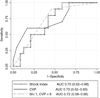
Results: Thirty-four volume expansions were observed in 25 patients. A CVP of 8 mm Hg or greater and a shock index of 1 beat min(-1) mm Hg(-1) or less individually had a good negative predictive value (83% and 88%, respectively). Of 34 volume expansions, the combination of both a high CVP and a low shock index was extremely unlikely to elicit hemodynamic response (negative predictive value, 93%; P = .02).
Conclusions: Volume expansion in patients with early septic shock with a CVP of 8 mm Hg or greater and a shock index of 1 beat min(-1) mm Hg(-1) or less is unlikely to lead to an increase in cardiac index.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Maitland K, Kiguli S, Opoka RO, Engoru C, Olupot-Olupot P, Akech SO, et al. Mortality after fluid bolus in African children with severe infection. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(26):2483–2495. - PubMed
-
- Humphrey H, Hall J, Sznajder I, Silverstein M, Wood L. Improved survival in ARDS patients associated with a reduction in pulmonary capillary wedge pressure. Chest. 1990;97(5):1176–1180. - PubMed
-
- Wiedemann HP, Wheeler AP, Bernard GR, Thompson BT, Hayden D, deBoisblanc B, et al. Comparison of two fluid-management strategies in acute lung injury. N Engl J Med. 2006;354(24):2564–2575. - PubMed
-
- Rivers E, Nguyen B, Havstad S, Ressler J, Muzzin A, Knoblich B, et al. Early goal–directed therapy in the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2001;345(19):1368–1377. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

