Long-timescale dynamics and regulation of Sec-facilitated protein translocation
- PMID: 23084746
- PMCID: PMC3483636
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2012.08.039
Long-timescale dynamics and regulation of Sec-facilitated protein translocation
Abstract
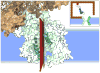
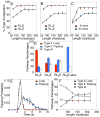
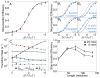
We present a coarse-grained modeling approach that spans the nanosecond- to minute-timescale dynamics of cotranslational protein translocation. The method enables direct simulation of both integral membrane protein topogenesis and transmembrane domain (TM) stop-transfer efficiency. Simulations reveal multiple kinetic pathways for protein integration, including a mechanism in which the nascent protein undergoes slow-timescale reorientation, or flipping, in the confined environment of the translocon channel. Competition among these pathways gives rise to the experimentally observed dependence of protein topology on ribosomal translation rate and protein length. We further demonstrate that sigmoidal dependence of stop-transfer efficiency on TM hydrophobicity arises from local equilibration of the TM across the translocon lateral gate, and it is predicted that slowing ribosomal translation yields decreased stop-transfer efficiency in long proteins. This work reveals the balance between equilibrium and nonequilibrium processes in protein targeting, and it provides insight into the molecular regulation of the Sec translocon.
Copyright © 2012 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Beckmann R, Spahn CM, Eswar N, Helmers J, Penczek PA, Sali A, Frank J, Blobel G. Architecture of the protein-conducting channel associated with the translating 80S ribosome. Cell. 2001;107:361–372. - PubMed
-
- Beltzer JP, Fiedler K, Fuhrer C, Geffen I, Handschin C, Wessels HP, Spiess M. Charged residues are major determinants of the transmembrane orientation of a signal-anchor sequence. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:973–978. - PubMed
-
- Berg Bvd, Clemons WM, Collinson I, Modis Y, Hartmann E, Harrison SC, Rapoport TA. X-ray structure of a protein-conducting channel. Nature. 2004;427:36–44. - PubMed
-
- Bieker KL, Silhavy TJ. PrlA (SecY) and PrlG (SecE) interact directly and function sequentially during protein translocation in E. coli. Cell. 1990;61:833–842. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

