Neurosteroids, stress and depression: potential therapeutic opportunities
- PMID: 23085210
- PMCID: PMC3591791
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2012.10.005
Neurosteroids, stress and depression: potential therapeutic opportunities
Abstract
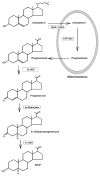
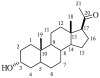
Neurosteroids are potent and effective neuromodulators that are synthesized from cholesterol in the brain. These agents and their synthetic derivatives influence the function of multiple signaling pathways including receptors for γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and glutamate, the major inhibitory and excitatory neurotransmitters in the central nervous system (CNS). Increasing evidence indicates that dysregulation of neurosteroid production plays a role in the pathophysiology of stress and stress-related psychiatric disorders, including mood and anxiety disorders. In this paper, we review the mechanisms of neurosteroid action in brain with an emphasis on those neurosteroids that potently modulate the function of GABA(A) receptors. We then discuss evidence indicating a role for GABA and neurosteroids in stress and depression, and focus on potential strategies that can be used to manipulate CNS neurosteroid synthesis and function for therapeutic purposes.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Agis-Balboa RC, Pinna G, Pibiri F, Kadriu B, Costa E, Guidotti A. Down-regulation of neurosteroid biosynthesis in corticolimbic circuits mediates social isolation-induced behavior in mice. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2007;104:18736–18741. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Airan RD, Meltzer LA, Roy M, Gong Y, Chen H, Deisseroth K. High-speed imaging reveals neurophysiological links to behavior in an animal model of depression. Science. 2007;317:819–823. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

