Exploiting genes and functional diversity of chlorogenic acid and luteolin biosyntheses in Lonicera japonica and their substitutes
- PMID: 23085319
- PMCID: PMC7138419
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.09.051
Exploiting genes and functional diversity of chlorogenic acid and luteolin biosyntheses in Lonicera japonica and their substitutes
Abstract
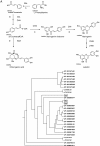
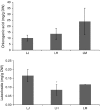
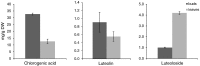
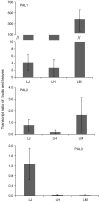
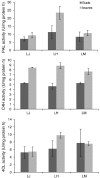
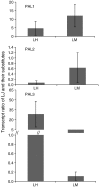
Chlorogenic acids (CGAs) and luteolin are active compounds in Lonicera japonica, a plant of high medicinal value in traditional Chinese medicine. This study provides a comprehensive overview of gene families involved in chlorogenic acid and luteolin biosynthesis in L. japonica, as well as its substitutes Lonicera hypoglauca and Lonicera macranthoides. The gene sequence feature and gene expression patterns in various tissues and buds of the species were characterized. Bioinformatics analysis revealed that 14 chlorogenic acid and luteolin biosynthesis-related genes were identified from the L. japonica transcriptome assembly. Phylogenetic analyses suggested that the function of individual gene could be differentiation and induce active compound diversity. Their orthologous genes were also recognized in L. hypoglauca and L. macranthoides genomic datasets, except for LHCHS1 and LMC4H2. The expression patterns of these genes are different in the tissues of L. japonica, L. hypoglauca and L. macranthoides. Results also showed that CGAs were controlled in the first step of biosynthesis, whereas both steps controlled luteolin in the bud of L. japonica. The expression of LJFNS2 exhibited positive correlation with luteolin levels in L. japonica. This study provides significant information for understanding the functional diversity of gene families involved in chlorogenic acid and the luteolin biosynthesis, active compound diversity of L. japonica and its substitutes, and the different usages of the three species.
Keywords: Chlorogenic acid; DNA; DP; Gene expression; Honeysuckle; Luteolin; ORF; Othologous genes; PCR; RACE; RNA; Selaginella pulvinta; Sp; TPP; TPS; cDNA; complementary DNA; degenerate primer; deoxyribonucleic acids; open reading frame; polymerase chain reaction; raid amplification of cDNA ends; ribonucleic acids; trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase; trehalose-6-phosphate synthase; trehalose-6-phosphate synthase gene.
Copyright © 2012. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures

References
-
- Bai G.B., Peng X.X., Li W.D., Wang W.Q. Cloning and characterization of a cDNA coding a hydroxycinnamoyl-CoA quinate hydroxycinnamoyl transferase involved in chlorogenic acid biosynthesis in Lonicera japonica. Planta Med. 2010;76:1921–1926. - PubMed
-
- Bjellqvist B., Basse B., Olsen E., Celis J.E. Reference points for comparisons of two-dimensional maps of proteins from different human cell types defined in a pH scale where isoelectric points correlate with polypeptide compositions. Electrophoresis. 1994;15:529–539. - PubMed
-
- Brueske C.H. Phenylalanine ammonia lyase activity in tomatoroots infected and resistant to the root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne incognita. Physiol. Plant Pathol. 1980;16:409–414.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

