Insight into estrogen receptor beta-beta and alpha-beta homo- and heterodimerization: A combined molecular dynamics and sequence analysis study
- PMID: 23085454
- PMCID: PMC4127405
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpc.2012.09.002
Insight into estrogen receptor beta-beta and alpha-beta homo- and heterodimerization: A combined molecular dynamics and sequence analysis study
Abstract
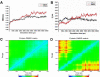
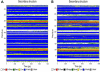
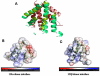
Biological effects of estrogenic ligands are transduced by two estrogen receptors, ERα and ERβ; they transactivate as dimers. Since ERββ and ERαβ homo- and heterodimers are known to exhibit anti-proliferative effects, we characterized their dimerization interface in atomic details and explored their ligand induced conformational dynamics. ERαβ heterodimer is found to be relatively more stable than the ERββ homodimer and the observed differences are mainly due to loop dynamics. The principal component analysis reveals that, in the essential subspace, the homo- and heterodimer dynamics are distinctively different. The core recognition groove of the dimer interface, formed by helix 9 and helix 10/11, remains unaltered in both homo- and heterodimers. The dimerization surfaces are found to be highly conserved in eukaryotic lineages. Phylogenetic patterns for ERα appear to be very much similar to that of ERβ which signifies that the formation of functional heterodimer is evolutionary selected.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
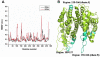



Similar articles
-
Intermolecular interactions identify ligand-selective activity of estrogen receptor alpha/beta dimers.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Dec 2;105(48):19012-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0807274105. Epub 2008 Nov 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 19022902 Free PMC article.
-
A Computational-Based Approach to Identify Estrogen Receptor α/β Heterodimer Selective Ligands.Mol Pharmacol. 2018 Mar;93(3):197-207. doi: 10.1124/mol.117.108696. Epub 2018 Jan 2. Mol Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29295894 Free PMC article.
-
Single-chain estrogen receptors (ERs) reveal that the ERalpha/beta heterodimer emulates functions of the ERalpha dimer in genomic estrogen signaling pathways.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Sep;24(17):7681-94. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.17.7681-7694.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15314175 Free PMC article.
-
Lessons learnt from structural studies of the oestrogen receptor.Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006 Mar;20(1):1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2005.09.002. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006. PMID: 16522516 Review.
-
Reflections on the discovery and significance of estrogen receptor beta.Endocr Rev. 2005 May;26(3):465-78. doi: 10.1210/er.2004-0027. Epub 2005 Apr 27. Endocr Rev. 2005. PMID: 15857973 Review.
Cited by
-
Estrogen directly and specifically downregulates NaPi-IIa through the activation of both estrogen receptor isoforms (ERα and ERβ) in rat kidney proximal tubule.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2015 Mar 15;308(6):F522-34. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00386.2014. Epub 2015 Jan 21. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25608964 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen Biosynthesis and Signal Transduction in Ovarian Disease.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Mar 1;13:827032. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.827032. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35299973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Targeting of Ovarian Cancer Stem Cells Using Estrogen Receptor Beta Agonist.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 28;23(13):7159. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137159. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35806169 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial p38β and manganese superoxide dismutase interaction mediated by estrogen in cardiomyocytes.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 22;9(1):e85272. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085272. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24465521 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional characteristics of oestrogen receptor β splice variants: Implications for the ageing brain.J Neuroendocrinol. 2018 Feb;30(2):10.1111/jne.12488. doi: 10.1111/jne.12488. J Neuroendocrinol. 2018. PMID: 28514502 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Heldring N, Pike A, Andersson S, Matthews J, Cheng G, Hartman J, Tujague M, Ström A, Treuter E, Warner M, Gustafsson JA. Estrogen receptors: how do they signal and what are their targets. Physiol. Rev. 2007;87:905–931. - PubMed
-
- Arts J, Kuiper GGJM, Janssen JMMF, Gustafsson JA, Lowik CWGM, Pols HAP, Leeuwen JPTMV. Differential expression of Estrogen receptors α and β mRNA during differentiation of human osteoblast SV-HFO cells. Endocrinology. 1997;138:5067–5070. - PubMed
-
- Enmark E, Pelto-Huikko M, Grandien K, Lagercrantz S, Lagercrantz J, Fried G, Nordenskjold M, Gustafsson JA. Human estrogen receptor β – gene structure, chromosomal localization, expression pattern. J. Clin. Endo. Met. 1997;82:4258–4265. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

