Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR cascade inhibitors: how mutations can result in therapy resistance and how to overcome resistance
- PMID: 23085539
- PMCID: PMC3717945
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.659
Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR cascade inhibitors: how mutations can result in therapy resistance and how to overcome resistance
Abstract
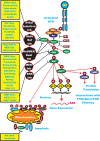
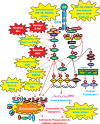
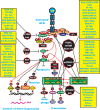
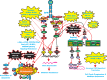
The Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR cascades are often activated by genetic alterations in upstream signaling molecules such as receptor tyrosine kinases (RTK). Targeting these pathways is often complex and can result in pathway activation depending on the presence of upstream mutations (e.g., Raf inhibitors induce Raf activation in cells with wild type (WT) RAF in the presence of mutant, activated RAS) and rapamycin can induce Akt activation. Targeting with inhibitors directed at two constituents of the same pathway or two different signaling pathways may be a more effective approach. This review will first evaluate potential uses of Raf, MEK, PI3K, Akt and mTOR inhibitors that have been investigated in pre-clinical and clinical investigations and then discuss how cancers can become insensitive to various inhibitors and potential strategies to overcome this resistance.
Figures
References
-
- Barretina J, Caponigro G, Stransky N, Venkatesan K, Margolin AA, Kim S, Wilson CJ, Lehár J, Kryukov GV, Sonkin D, Reddy A, Liu M, Murray L, Berger MF, Monahan JE, Morais P, et al. The Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia enables predictive modelling of anticancer drug sensitivity. Nature. 2012;483:603–607. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chappell WH, Steelman LS, Long JM, Kempf RC, Abrams SL, Franklin RA, Bäsecke J, Stivala F, Donia M, Fagone P, Malaponte G, Mazzarino MC, Nicoletti F, Libra M, Maksimovic-Ivanic D, Mijatovic S, et al. Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR Inhibitors: Rationale and Importance to Inhibiting These Pathways in Human Health. Oncotarget. 2011;2:135–164. - PMC - PubMed
-
- McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Kempf CR, Chappell W, Abrams SL, Stivala F, Malaponte G, Nicoletti F, Libra M, Bäsecke J, Maksimovic-Ivanic D, Mijatovic S, Montalto G, Cervello M, Cocco L, Martelli AM. Therapeutic resistance resulting from mutations in Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways. J Cell Physiol. 2011;226:2762–2781. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

