A phase I study on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of higenamine in healthy Chinese subjects
- PMID: 23085737
- PMCID: PMC4011356
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2012.114
A phase I study on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of higenamine in healthy Chinese subjects
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and safety of higenamine, an active ingredient of Aconite root, in healthy Chinese volunteers.
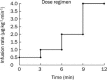
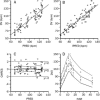
Methods: Ten subjects received continuous, intravenous infusion of higenamine at gradually escalating doses from 0.5 to 4.0 μg·kg(-1)·min(-1), each dose was given for 3 min. Blood and urine samples were collected at designated time points to measure the concentrations of higenamine. Pharmacodynamics was assessed by measuring the subject's heart rate. A nonlinear mixed-effect modeling approach, using the software Phoenix NLME, was used to model the plasma concentration-time profiles and heart rate.
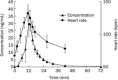
Results: Peak concentrations (C(max)) of higenamine ranged from 15.1 to 44.0 ng/mL. The half-life of higenamine was 0.133 h (range, 0.107-0.166 h), while the area under concentration-time curve (AUC), extrapolated to infinity, was 5.39 ng·h·mL(-1) (range, 3.2-6.8 ng·h·mL(-1)). The volume of distribution (V) was 48 L (range, 30.8-80.6 L). The total clearance (CL) was 249 L/h (range, 199-336 L/h). Within 8 h, 9.3% (range, 4.6%-12.4%) of higenamine was recovered in the urine. The pharmacokinetics of higenamine was successfully described using a two-compartment model with nonlinear clearance. In the pharmacodynamic model, heart rates were related to the plasma drug concentrations using a simple direct effect model with baseline. The E(0), E(max), and EC(50) were 68 bpm, 73 bpm and 8.1 μg/L, respectively.
Conclusion: Higenamine has desirable pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic characteristics. The results provide important information for future clinical studies on higenamine.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pharmacokinetics of higenamine in rabbits.Biopharm Drug Dispos. 1996 Dec;17(9):791-803. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1099-081X(199612)17:9<791::AID-BDD993>3.0.CO;2-T. Biopharm Drug Dispos. 1996. PMID: 8968531
-
Applications of Higenamine in pharmacology and medicine.J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 Jan 20;196:242-252. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.12.033. Epub 2016 Dec 19. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28007527 Review.
-
Blood-to-muscle distribution and urinary excretion of higenamine in rats.Drug Test Anal. 2021 Oct;13(10):1776-1782. doi: 10.1002/dta.3132. Epub 2021 Sep 7. Drug Test Anal. 2021. PMID: 34309209
-
Population pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of bivalirudin in young healthy Chinese volunteers.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012 Nov;33(11):1387-94. doi: 10.1038/aps.2012.37. Epub 2012 Jun 4. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012. PMID: 22659624 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
[Effects of higenamine on the cardio-circulatory system].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2003 Oct;28(10):910-3. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2003. PMID: 15620176 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Presence of higenamine in beetroot containing 'foodstuffs' and the implication for WADA-relevant anti-doping testing.Drug Test Anal. 2023 Feb;15(2):173-180. doi: 10.1002/dta.3383. Epub 2022 Oct 25. Drug Test Anal. 2023. PMID: 36218291 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacometrics: a quantitative tool of pharmacological research.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012 Nov;33(11):1337-8. doi: 10.1038/aps.2012.149. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012. PMID: 23128515 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Pharmacological effects of higenamine based on signalling pathways and mechanism of action.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 15;13:981048. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.981048. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36188548 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Higenamine in Plants as a Source of Unintentional Doping.Plants (Basel). 2022 Jan 27;11(3):354. doi: 10.3390/plants11030354. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35161335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dietary Supplements as Source of Unintentional Doping.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Apr 22;2022:8387271. doi: 10.1155/2022/8387271. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35496041 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Picano E. Stress echocardiography from pathophysiological toy to diagnostic tool. Circulation. 1992;85:1604–12. - PubMed
-
- Zoghbi GJ, Iskandrian AE. Selective adenosine agonists and myocardial perfusion imaging. J Nucl Cardiol. 2012;19:126–41. - PubMed
-
- Elhendy A, Bax JJ, Poldermans D. Dobutamine stress myocardial perfusion imaging in coronary artery disease. J Nucl Med. 2002;43:1634–46. - PubMed
-
- Cortigiani L, Zanetti L, Bigi R, Desideri A, Fiorentini C, Nannini E. Safety and feasibility of dobutamine and dipyridamole stress echocardiography in hypertensive patients. J Hypertens. 2002;20:1423–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

