Noninvasive Raman spectroscopy of rat tibiae: approach to in vivo assessment of bone quality
- PMID: 23085899
- PMCID: PMC3434704
- DOI: 10.1117/1.JBO.17.9.090502
Noninvasive Raman spectroscopy of rat tibiae: approach to in vivo assessment of bone quality
Abstract
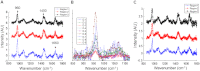
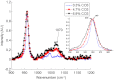
We report on in vivo noninvasive Raman spectroscopy of rat tibiae using robust fiber-optic Raman probes and holders designed for transcutaneous Raman measurements in small animals. The configuration allows placement of multiple fibers around a rat leg, maintaining contact with the skin. Bone Raman data are presented for three regions of the rat tibia diaphysis with different thicknesses of overlying soft tissue. The ability to perform in vivo noninvasive Raman measurement and evaluation of subtle changes in bone composition is demonstrated with rat leg phantoms in which the tibia has carbonated hydroxylapatite, with different carbonate contents. Our data provide proof of the principle that small changes in bone composition can be monitored through soft tissue at anatomical sites of interest in biomedical studies.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transcutaneous fiber optic Raman spectroscopy of bone using annular illumination and a circular array of collection fibers.J Biomed Opt. 2006 Nov-Dec;11(6):060502. doi: 10.1117/1.2400233. J Biomed Opt. 2006. PMID: 17212521
-
Transcutaneous Raman spectroscopy of murine bone in vivo.Appl Spectrosc. 2009 Mar;63(3):286-95. doi: 10.1366/000370209787599013. Appl Spectrosc. 2009. PMID: 19281644 Free PMC article.
-
Subsurface Raman spectroscopy and mapping using a globally illuminated non-confocal fiber-optic array probe in the presence of Raman photon migration.Appl Spectrosc. 2006 Feb;60(2):109-14. doi: 10.1366/000370206776023340. Appl Spectrosc. 2006. PMID: 16542561
-
The optical fiber tip: an inherently light-coupled microscopic platform for micro- and nanotechnologies.Adv Mater. 2014 Jun 18;26(23):3798-820. doi: 10.1002/adma.201304605. Epub 2014 Mar 5. Adv Mater. 2014. PMID: 24599822 Review.
-
Fiber optic probes for biomedical optical spectroscopy.J Biomed Opt. 2003 Jan;8(1):121-47. doi: 10.1117/1.1528207. J Biomed Opt. 2003. PMID: 12542388 Review.
Cited by
-
Near infrared spectroscopic assessment of loosely and tightly bound cortical bone water.Analyst. 2020 May 21;145(10):3713-3724. doi: 10.1039/c9an02491c. Epub 2020 Apr 28. Analyst. 2020. PMID: 32342066 Free PMC article.
-
Do laser/LED phototherapies influence the outcome of the repair of surgical bone defects grafted with biphasic synthetic microgranular HA + β-tricalcium phosphate? A Raman spectroscopy study.Lasers Med Sci. 2014 Sep;29(5):1575-84. doi: 10.1007/s10103-014-1563-y. Epub 2014 Mar 14. Lasers Med Sci. 2014. PMID: 24627284
-
Raman spectroscopy delineates radiation-induced injury and partial rescue by amifostine in bone: a murine mandibular model.J Bone Miner Metab. 2015 May;33(3):279-84. doi: 10.1007/s00774-014-0599-1. Epub 2014 Oct 16. J Bone Miner Metab. 2015. PMID: 25319554 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue Phantoms for Biomedical Applications in Raman Spectroscopy: A Review.Biomed Eng Comput Biol. 2020 Aug 19;11:1179597220948100. doi: 10.1177/1179597220948100. eCollection 2020. Biomed Eng Comput Biol. 2020. PMID: 32884391 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overconstrained library-based fitting method reveals age- and disease-related differences in transcutaneous Raman spectra of murine bones.J Biomed Opt. 2013 Jul;18(7):077001. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.18.7.077001. J Biomed Opt. 2013. PMID: 23817761 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gamsjäger S., et al. , “Raman application in bone imaging,” in Raman Spectroscopy for Soft Matter Applications, pp. 225–267, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken, New Jersey: (2009).
-
- Morris M., “Raman spectroscopy of bone and cartilage,” in Emerging Raman Applications and Techniques in Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Fields, Matousek P., Morris M. D., Eds., pp. 347–364, Springer, Berlin Heidelberg: (2010).

