Mechanisms underlying lineage commitment and plasticity of human γδ T cells
- PMID: 23085943
- PMCID: PMC4003171
- DOI: 10.1038/cmi.2012.42
Mechanisms underlying lineage commitment and plasticity of human γδ T cells
Abstract
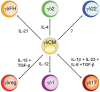
Phenotypic and functional heterogeneity are the hallmarks of effector and memory T cells. Upon antigen stimulation, γδ T cells differentiate into two major types of memory T cells: central memory cells, which patrol the blood and secondary lymphoid organs, and effector memory cells, which migrate to peripheral tissues. γδ T cells display in vitro a certain degree of plasticity in their function that is reminiscent of that which is observed in conventional CD4 T cells. Similar to CD4 T cells, in which a plethora of specialized subsets affect the host response, γδ T cells may readily and rapidly assume distinct Th1-, Th2-, Th17-, T(FH) and T regulatory-like effector functions, suggesting that they profoundly influence cell-mediated and humoral immune responses. In addition to differences in cytokine repertoire, γδ T cells exhibit diversity in homing, such as migration to lymph node follicles, to help B cells versus migration to inflamed tissues. Here, we review our current understanding of γδ T-cell lineage heterogeneity and flexibility, with an emphasis on the human system, and propose a classification of effector γδ T cells based on distinct functional phenotypes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Heterogeneity of CD4+ memory T cells: functional modules for tailored immunity.Eur J Immunol. 2009 Aug;39(8):2076-82. doi: 10.1002/eji.200939722. Eur J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19672903 Review.
-
CD4+ CD25+ Treg cells inhibit human memory gammadelta T cells to produce IFN-gamma in response to M tuberculosis antigen ESAT-6.Blood. 2008 Jun 15;111(12):5629-36. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-02-139899. Epub 2008 Apr 3. Blood. 2008. PMID: 18388182
-
Phenotypic and functional plasticity of gamma-delta (γδ) T cells in inflammation and tolerance.Int Rev Immunol. 2014 Nov-Dec;33(6):537-58. doi: 10.3109/08830185.2013.863306. Epub 2013 Dec 19. Int Rev Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24354324 Review.
-
Identification of a human Th1-like IFNγ-secreting Treg subtype deriving from effector T cells.J Autoimmun. 2012 Dec;39(4):377-87. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2012.06.004. Epub 2012 Jul 22. J Autoimmun. 2012. PMID: 22824211
-
Immune response of human propagated gammadelta-T-cells to neuroblastoma recommend the Vdelta1+ subset for gammadelta-T-cell-based immunotherapy.J Immunother. 2008 Nov-Dec;31(9):896-905. doi: 10.1097/CJI.0b013e31818955ad. J Immunother. 2008. PMID: 18832998
Cited by
-
Harnessing Unconventional T Cells for Immunotherapy of Tuberculosis.Front Immunol. 2020 Sep 3;11:2107. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.02107. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33013888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The porcine innate immune system: an update.Dev Comp Immunol. 2014 Aug;45(2):321-43. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2014.03.022. Epub 2014 Apr 4. Dev Comp Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24709051 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual Face of Vγ9Vδ2-T Cells in Tumor Immunology: Anti- versus Pro-Tumoral Activities.Front Immunol. 2017 Aug 28;8:1041. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01041. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28894450 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Downregulation of miRNA17-92 cluster marks Vγ9Vδ2 T cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2018 Oct 22;20(1):236. doi: 10.1186/s13075-018-1740-7. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 30348222 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotypic Changes of Peripheral γδ T Cell and Its Subsets in Patients With Coronary Artery Disease.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 8;13:900334. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.900334. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35874761 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bonneville M, O'Brien RL, Born WK. γδ T cell effector functions: a blend of innate programming and acquired plasticity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010;10:467–478. - PubMed
-
- Sireci G, Champagne E, Fournié JJ, Dieli F, Salerno A. Patterns of phosphoantigen stimulation of human Vγ9Vδ2 T cell clones include Th0 cytokines. Hum Immunol. 1997;58:70–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

