MicroRNA 339 down-regulates μ-opioid receptor at the post-transcriptional level in response to opioid treatment
- PMID: 23085997
- PMCID: PMC3545525
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.12-213439
MicroRNA 339 down-regulates μ-opioid receptor at the post-transcriptional level in response to opioid treatment
Abstract
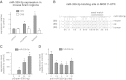
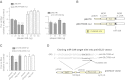
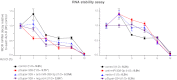
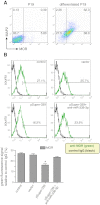
μ-Opioid receptor (MOR) level is directly related to the function of opioid drugs, such as morphine and fentanyl. Although agonist treatment generally does not affect transcription of mor, previous studies suggest that morphine can affect the translation efficiency of MOR transcript via microRNAs (miRNAs). On the basis of miRNA microarray analyses of the hippocampal total RNA isolated from mice chronically treated with μ-opioid agonists, we found a miRNA (miR-339-3p) that was consistently and specifically increased by morphine (2-fold) and by fentanyl (3.8-fold). miR-339-3p bound to the MOR 3'-UTR and specifically suppressed reporter activity. Suppression was blunted by adding miR-339-3p inhibitor or mutating the miR-339-3p target site. In cells endogenously expressing MOR, miR-339-3p inhibited the production of MOR protein by destabilizing MOR mRNA. Up-regulation of miR-339-3p by fentanyl (EC(50)=0.75 nM) resulted from an increase in primary miRNA transcript. Mapping of the miR-339-3p primary RNA and its promoter revealed that the primary miR-339-3p was embedded in a noncoding 3'-UTR region of an unknown host gene and was coregulated by the host promoter. The identified promoter was activated by opioid agonist treatment (10 nM fentanyl or 10 μM morphine), a specific effect blocked by the opioid antagonist naloxone (10 μM). Taken together, these results suggest that miR-339-3p may serve as a negative feedback modulator of MOR signals by regulating intracellular MOR biosynthesis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Morphine modulates the expression of mu-opioid receptor exon 5-associated full-length C-terminal splice variants by upregulating miR-378a-3p.FASEB J. 2020 Mar;34(3):4540-4556. doi: 10.1096/fj.201901879RR. Epub 2020 Jan 30. FASEB J. 2020. PMID: 31999011 Free PMC article.
-
Morphine regulates expression of μ-opioid receptor MOR-1A, an intron-retention carboxyl terminal splice variant of the μ-opioid receptor (OPRM1) gene via miR-103/miR-107.Mol Pharmacol. 2014 Feb;85(2):368-80. doi: 10.1124/mol.113.089292. Epub 2013 Dec 3. Mol Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24302561 Free PMC article.
-
Opioid-induced regulation of mu-opioid receptor gene expression in the MCF-7 breast cancer cell line.Biochem Cell Biol. 2008 Jun;86(3):217-26. doi: 10.1139/o08-001. Biochem Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18523482
-
Ligand-Free Signaling of G-Protein-Coupled Receptors: Relevance to μ Opioid Receptors in Analgesia and Addiction.Molecules. 2022 Sep 8;27(18):5826. doi: 10.3390/molecules27185826. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36144565 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Direct involvement of the supraspinal phosphoinositide 3-kinase/phospholipase C gamma 1 pathway in the mu-opioid receptor agonist-induced supraspinal antinociception in the mouse].Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2003 Jun;23(3):121-8. Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2003. PMID: 12884752 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
The Emerging Perspective of Morphine Tolerance: MicroRNAs.Pain Res Manag. 2019 Apr 30;2019:9432965. doi: 10.1155/2019/9432965. eCollection 2019. Pain Res Manag. 2019. PMID: 31182985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel biomarkers to assess in utero effects of maternal opioid use: First steps toward understanding short- and long-term neurodevelopmental sequelae.Genes Brain Behav. 2019 Jul;18(6):e12583. doi: 10.1111/gbb.12583. Epub 2019 Jun 11. Genes Brain Behav. 2019. PMID: 31119847 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroepigenetics and addiction.Handb Clin Neurol. 2018;148:747-765. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-64076-5.00048-X. Handb Clin Neurol. 2018. PMID: 29478612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Alterations in Prescription Opioid Misuse: New Strategies for Precision Pain Management.Genes (Basel). 2021 Aug 10;12(8):1226. doi: 10.3390/genes12081226. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34440400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of Circulating miRNAs Differentially Regulated by Opioid Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Sep 16;18(9):1991. doi: 10.3390/ijms18091991. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28926935 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Law P. Y., Loh H. H., Wei L. N. (2004) Insights into the receptor transcription and signaling: implications in opioid tolerance and dependence. Neuropharmacology 47(Suppl. 1), 300–311 - PubMed
-
- Binyaminy B., Gafni M., Shapira M., Sarne Y. (2008) Agonist-specific down regulation of mu-opioid receptors: different cellular pathways are activated by different opioid agonists. Life Sci. 82, 831–839 - PubMed
-
- Kramer H. K., Simon E. J. (1999) Role of protein kinase C (PKC) in agonist-induced mu-opioid receptor down-regulation: II. Activation and involvement of the alpha, epsilon, and zeta isoforms of PKC. J. Neurochem. 72, 594–604 - PubMed
-
- Schmidt H., Schulz S., Klutzny M., Koch T., Handel M., Hollt V. (2000) Involvement of mitogen-activated protein kinase in agonist-induced phosphorylation of the mu-opioid receptor in HEK 293 cells. J. Neurochem. 74, 414–422 - PubMed
-
- Koch T., Kroslak T., Mayer P., Raulf E., Hollt V. (1997) Site mutation in the rat mu-opioid receptor demonstrates the involvement of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II in agonist-mediated desensitization. J. Neurochem. 69, 1767–1770 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

