PGC-1α improves glucose homeostasis in skeletal muscle in an activity-dependent manner
- PMID: 23086035
- PMCID: PMC3526021
- DOI: 10.2337/db12-0291
PGC-1α improves glucose homeostasis in skeletal muscle in an activity-dependent manner
Abstract
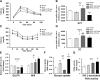
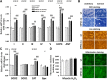
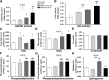
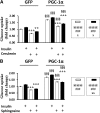
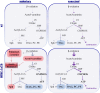
Metabolic disorders are a major burden for public health systems globally. Regular exercise improves metabolic health. Pharmacological targeting of exercise mediators might facilitate physical activity or amplify the effects of exercise. The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1α (PGC-1α) largely mediates musculoskeletal adaptations to exercise, including lipid refueling, and thus constitutes such a putative target. Paradoxically, forced expression of PGC-1α in muscle promotes diet-induced insulin resistance in sedentary animals. We show that elevated PGC-1α in combination with exercise preferentially improves glucose homeostasis, increases Krebs cycle activity, and reduces the levels of acylcarnitines and sphingosine. Moreover, patterns of lipid partitioning are altered in favor of enhanced insulin sensitivity in response to combined PGC-1α and exercise. Our findings reveal how physical activity improves glucose homeostasis. Furthermore, our data suggest that the combination of elevated muscle PGC-1α and exercise constitutes a promising approach for the treatment of metabolic disorders.
Figures
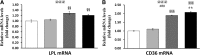

Comment in
-
Regulation of glycemic control by physical activity: a role for mitochondria?Diabetes. 2013 Jan;62(1):34-5. doi: 10.2337/db12-1209. Diabetes. 2013. PMID: 23258911 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bogers RP, Barte JC, Schipper CM, et al. Relationship between costs of lifestyle interventions and weight loss in overweight adults. Obes Rev 2010;11:51–61 - PubMed
-
- Kopelman PG. Obesity as a medical problem. Nature 2000;404:635–643 - PubMed
-
- Kahn BB, Alquier T, Carling D, Hardie DG. AMP-activated protein kinase: ancient energy gauge provides clues to modern understanding of metabolism. Cell Metab 2005;1:15–25 - PubMed
-
- Zhang BB, Zhou G, Li C. AMPK: an emerging drug target for diabetes and the metabolic syndrome. Cell Metab 2009;9:407–416 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

