Engineered ascorbate peroxidase as a genetically encoded reporter for electron microscopy
- PMID: 23086203
- PMCID: PMC3699407
- DOI: 10.1038/nbt.2375
Engineered ascorbate peroxidase as a genetically encoded reporter for electron microscopy
Abstract
Electron microscopy (EM) is the standard method for imaging cellular structures with nanometer resolution, but existing genetic tags are inactive in most cellular compartments or require light and can be difficult to use. Here we report the development of 'APEX', a genetically encodable EM tag that is active in all cellular compartments and does not require light. APEX is a monomeric 28-kDa peroxidase that withstands strong EM fixation to give excellent ultrastructural preservation. We demonstrate the utility of APEX for high-resolution EM imaging of a variety of mammalian organelles and specific proteins using a simple and robust labeling procedure. We also fused APEX to the N or C terminus of the mitochondrial calcium uniporter (MCU), a recently identified channel whose topology is disputed. These fusions give EM contrast exclusively in the mitochondrial matrix, suggesting that both the N and C termini of MCU face the matrix. Because APEX staining is not dependent on light activation, APEX should make EM imaging of any cellular protein straightforward, regardless of the size or thickness of the specimen.
Conflict of interest statement
Massachusetts Institute of Technology is seeking to file a patent application covering part of the information contained in this article.
Figures
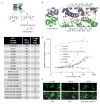



Comment in
-
A genetically encoded probe for EM.Nat Methods. 2012 Dec;9(12):1140-1. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2273. Nat Methods. 2012. PMID: 23355984 No abstract available.
References
-
- Hopkins C, Gibson A, Stinchcombe J, Futter C. Chimeric molecules employing horseradish peroxidase as reporter enzyme for protein localization in the electron microscope. Methods in enzymology. 2000;327:35. - PubMed
-
- De Mey J, Moeremans M, Geuens G, Nuydens R, De Brabander M. High resolution light and electron microscopic localization of tubulin with the IGS (immuno gold staining) method. Cell Biology International Reports. 1981;5:889–899. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P41 GM103412/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P41GM103412/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM42614/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P41RR004050/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR002250/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- GM065937/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM077465/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR004050/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM072881/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM065937/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM042614/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM072881/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- DP1 OD003961/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- GM077465/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

