Transcription factor family-based reconstruction of singleton regulons and study of the Crp/Fnr, ArsR, and GntR families in Desulfovibrionales genomes
- PMID: 23086211
- PMCID: PMC3536172
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01977-12
Transcription factor family-based reconstruction of singleton regulons and study of the Crp/Fnr, ArsR, and GntR families in Desulfovibrionales genomes
Abstract
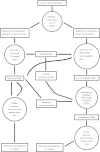
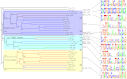
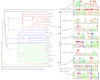
Accurate detection of transcriptional regulatory elements is essential for high-quality genome annotation, metabolic reconstruction, and modeling of regulatory networks. We developed a computational approach for reconstruction of regulons operated by transcription factors (TFs) from large protein families and applied this novel approach to three TF families in 10 Desulfovibrionales genomes. Phylogenetic analyses of 125 regulators from the ArsR, Crp/Fnr, and GntR families revealed that 65% of these regulators (termed reference TFs) are well conserved in Desulfovibrionales, while the remaining 35% of regulators (termed singleton TFs) are species specific and show a mosaic distribution. For regulon reconstruction in the group of singleton TFs, the standard orthology-based approach was inefficient, and thus, we developed a novel approach based on the simultaneous study of all homologous TFs from the same family in a group of genomes. As a result, we identified binding for 21 singleton TFs and for all reference TFs in all three analyzed families. Within each TF family we observed structural similarities between DNA-binding motifs of different reference and singleton TFs. The collection of reconstructed regulons is available at the RegPrecise database (http://regprecise.lbl.gov/RegPrecise/Desulfovibrionales.jsp).
Figures

Similar articles
-
RegPrecise 3.0--a resource for genome-scale exploration of transcriptional regulation in bacteria.BMC Genomics. 2013 Nov 1;14:745. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-745. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 24175918 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic reconstruction of the transcriptional regulatory network in Bacillus subtilis.J Bacteriol. 2013 Jun;195(11):2463-73. doi: 10.1128/JB.00140-13. Epub 2013 Mar 15. J Bacteriol. 2013. PMID: 23504016 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative genomics and evolution of regulons of the LacI-family transcription factors.Front Microbiol. 2014 Jun 11;5:294. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00294. eCollection 2014. Front Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24966856 Free PMC article.
-
The MocR-like transcription factors: pyridoxal 5'-phosphate-dependent regulators of bacterial metabolism.FEBS J. 2018 Nov;285(21):3925-3944. doi: 10.1111/febs.14599. Epub 2018 Jul 5. FEBS J. 2018. PMID: 29974999 Review.
-
FNR and its role in oxygen-regulated gene expression in Escherichia coli.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1990 Aug;6(4):399-428. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1990.tb04109.x. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1990. PMID: 2248796 Review.
Cited by
-
Reconstruction of novel transcription factor regulons through inference of their binding sites.BMC Bioinformatics. 2015 Sep 21;16:299. doi: 10.1186/s12859-015-0685-y. BMC Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 26388177 Free PMC article.
-
LurR is a regulator of the central lactate oxidation pathway in sulfate-reducing Desulfovibrio species.PLoS One. 2019 Apr 9;14(4):e0214960. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0214960. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30964892 Free PMC article.
-
An HcpR paralog of Desulfovibrio gigas provides protection against nitrosative stress.FEBS Open Bio. 2015 Jul 9;5:594-604. doi: 10.1016/j.fob.2015.07.001. eCollection 2015. FEBS Open Bio. 2015. PMID: 26273559 Free PMC article.
-
Functional genomics with a comprehensive library of transposon mutants for the sulfate-reducing bacterium Desulfovibrio alaskensis G20.mBio. 2014 May 27;5(3):e01041-14. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01041-14. mBio. 2014. PMID: 24865553 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Analysis of the IclR-Family of Bacterial Transcription Factors and Their DNA-Binding Motifs: Structure, Positioning, Co-Evolution, Regulon Content.Front Microbiol. 2021 Jun 10;12:675815. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.675815. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34177859 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rodionov DA, Novichkov PS, Stavrovskaya ED, Rodionova IA, Li X, Kazanov MD, Ravcheev DA, Gerasimova AV, Kazakov AE, Kovaleva GY, Permina EA, Laikova ON, Overbeek R, Romine MF, Fredrickson JK, Arkin AP, Dubchak I, Osterman AL, Gelfand MS. 2011. Comparative genomic reconstruction of transcriptional networks controlling central metabolism in the Shewanella genus. BMC Genomics 12(Suppl. 1): S3 doi:10.1186/1471-2164-12-S1-S3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

