Nutritional vitamin D use in chronic kidney disease: a survey of pediatric nephrologists
- PMID: 23086591
- PMCID: PMC4052461
- DOI: 10.1007/s00467-012-2307-5
Nutritional vitamin D use in chronic kidney disease: a survey of pediatric nephrologists
Abstract
Background: Vitamin D deficiency may contribute to risk of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and infections, in addition to known effects on mineral metabolism. Controversy remains regarding the use of nutritional vitamin D supplementation in chronic kidney disease (CKD), and the supplementation practices of pediatric nephrologists are unknown.
Methods: An electronic survey containing eight vignettes was sent to physician members of the International Pediatric Nephrology Association in 2011 to identify physician and patient characteristics that influence nephrologists to supplement CKD patients with nutritional vitamin D. Vignettes contained patient characteristics including light vs dark skin, CKD stage, cause of renal disease, parathyroid hormone (PTH), and 25(OH) vitamin D levels. Multivariate logistic generalized estimating equation regression was used to identify predictors of supplementation.
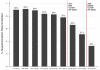
Results: Of 1,084 eligible physicians, 504 (46%) completed the survey. Supplementation was recommended in 73% of cases overall (ranging from 91% of those with vitamin D levels <10 ng/mL to 35% with levels >30). Greater CKD severity was associated with greater recommendation of supplementation, especially for patients with higher vitamin D levels (test for interaction p < 0.0001). PTH level above target for CKD stage was associated with greater recommendation to supplement in pre-dialysis CKD, but did not have an impact on recommendations in dialysis patients (test for interaction p < 0.0001). Skin color, cause of CKD, and albumin levels were not associated with supplementation recommendation.
Conclusions: Recommending nutritional vitamin D is common worldwide, driven by CKD stage and vitamin D and PTH levels. Future studies are needed to establish the risks and benefits of supplementation.
Figures

References
-
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes KDIGO guidelines: chapter 3.1: diagnosis of CKD-MBD: biochemical abnormalities. Kidney Int. 2009;76(Suppl 113):S22–S24. - PubMed
-
- Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative KDOQI clinical practice guidelines for bone metabolism and disease in chronic kidney disease: guideline 7. Prevention and treatment of vitamin D insufficiency and vitamin D deficiency in CKD patients. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003;42(Suppl 3):4.
-
- Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative KDOQI clinical practice guidelines for bone metabolism and disease in children with chronic kidney disease: guideline 8. Prevention and treatment of vitamin D insufficiency and vitamin D deficiency in CKD patients. Am J Kidney Dis. 2005;46(Suppl 1):4.
-
- Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative KDOQI clinical practice guideline for nutrition in children with CKD: 2008 update: recommendation 7: bone mineral and vitamin D requirements and therapy. Am J Kidney Dis. 2009;53(Suppl 2):3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

