Bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4) regulates RNA polymerase II serine 2 phosphorylation in human CD4+ T cells
- PMID: 23086925
- PMCID: PMC3522308
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.413047
Bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4) regulates RNA polymerase II serine 2 phosphorylation in human CD4+ T cells
Abstract
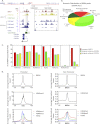
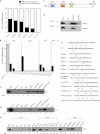
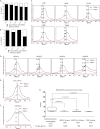
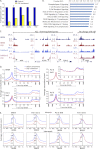
Transcriptional elongation by RNA polymerase II (Pol II) is regulated by positive transcription elongation factor b (P-TEFb) in association with bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4). We used genome-wide chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing in primary human CD4+ T cells to reveal that BRD4 co-localizes with Ser-2-phosphorylated Pol II (Pol II Ser-2) at both enhancers and promoters of active genes. Disruption of bromodomain-histone acetylation interactions by JQ1, a small-molecule bromodomain inhibitor, resulted in decreased BRD4 binding, reduced Pol II Ser-2, and reduced expression of lineage-specific genes in primary human CD4+ T cells. A large number of JQ1-disrupted BRD4 binding regions exhibited diacetylated H4 (lysine 5 and -8) and H3K27 acetylation (H3K27ac), which correlated with the presence of histone acetyltransferases and deacetylases. Genes associated with BRD4/H3K27ac co-occupancy exhibited significantly higher activity than those associated with H3K27ac or BRD4 binding alone. Comparison of BRD4 binding in T cells and in human embryonic stem cells revealed that enhancer BRD4 binding sites were predominantly lineage-specific. Our findings suggest that BRD4-driven Pol II phosphorylation at serine 2 plays an important role in regulating lineage-specific gene transcription in human CD4+ T cells.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Disrupting the interaction of BRD4 with diacetylated Twist suppresses tumorigenesis in basal-like breast cancer.Cancer Cell. 2014 Feb 10;25(2):210-25. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2014.01.028. Cancer Cell. 2014. PMID: 24525235 Free PMC article.
-
Histone cross-talk connects protein phosphatase 1α (PP1α) and histone deacetylase (HDAC) pathways to regulate the functional transition of bromodomain-containing 4 (BRD4) for inducible gene expression.J Biol Chem. 2014 Aug 15;289(33):23154-23167. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.570812. Epub 2014 Jun 17. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24939842 Free PMC article.
-
BRD4 assists elongation of both coding and enhancer RNAs by interacting with acetylated histones.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2014 Dec;21(12):1047-57. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2912. Epub 2014 Nov 10. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 25383670 Free PMC article.
-
Bromodomain 4: a cellular Swiss army knife.J Leukoc Biol. 2016 Oct;100(4):679-686. doi: 10.1189/jlb.2RI0616-250R. Epub 2016 Jul 22. J Leukoc Biol. 2016. PMID: 27450555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The double bromodomain-containing chromatin adaptor Brd4 and transcriptional regulation.J Biol Chem. 2007 May 4;282(18):13141-5. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R700001200. Epub 2007 Feb 28. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17329240 Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic drug discovery: breaking through the immune barrier.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2016 Dec;15(12):835-853. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2016.185. Epub 2016 Oct 21. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2016. PMID: 27765940 Review.
-
Enhanced Antitumoral Activity of Encapsulated BET Inhibitors When Combined with PARP Inhibitors for the Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast and Ovarian Cancers.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Sep 15;14(18):4474. doi: 10.3390/cancers14184474. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36139634 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of bromodomain-containing protein 4 enhances the migration of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells by inducing cell autophagy.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022 Dec 15;14(12):2340-2352. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i12.2340. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36568944 Free PMC article.
-
Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors: From Epigenome to Bedside.Mol Cancer Res. 2019 Jul;17(7):1417-1428. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-19-0147. Epub 2019 Apr 25. Mol Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31023785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancer-Mediated Formation of Nuclear Transcription Initiation Domains.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 18;23(16):9290. doi: 10.3390/ijms23169290. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36012554 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hochheimer A., Tjian R. (2003) Diversified transcription initiation complexes expand promoter selectivity and tissue-specific gene expression. Genes Dev. 17, 1309–1320 - PubMed
-
- Hirose Y., Ohkuma Y. (2007) Phosphorylation of the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II plays central roles in the integrated events of eucaryotic gene expression. J. Biochem. 141, 601–608 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

