Mitochondrial protein acylation and intermediary metabolism: regulation by sirtuins and implications for metabolic disease
- PMID: 23086951
- PMCID: PMC3522244
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.R112.404863
Mitochondrial protein acylation and intermediary metabolism: regulation by sirtuins and implications for metabolic disease
Abstract
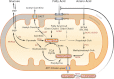
The sirtuins are a family of NAD(+)-dependent protein deacetylases that regulate cell survival, metabolism, and longevity. Three sirtuins, SIRT3-5, localize to mitochondria. Expression of SIRT3 is selectively activated during fasting and calorie restriction. SIRT3 regulates the acetylation level and enzymatic activity of key metabolic enzymes, such as acetyl-CoA synthetase, long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, and 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase 2, and enhances fat metabolism during fasting. SIRT5 exhibits demalonylase/desuccinylase activity, and lysine succinylation and malonylation are abundant mitochondrial protein modifications. No convincing enzymatic activity has been reported for SIRT4. Here, we review the emerging role of mitochondrial sirtuins as metabolic sensors that respond to changes in the energy status of the cell and modulate the activities of key metabolic enzymes via protein deacylation.
Figures
References
-
- Zhao S., Xu W., Jiang W., Yu W., Lin Y., Zhang T., Yao J., Zhou L., Zeng Y., Li H., Li Y., Shi J., An W., Hancock S. M., He F., Qin L., Chin J., Yang P., Chen X., Lei Q., Xiong Y., Guan K.-L. (2010) Regulation of cellular metabolism by protein lysine acetylation. Science 327, 1000–1004 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Frye R. A. (1999) Characterization of five human cDNAs with homology to the yeast SIR2 gene: Sir2-like proteins (sirtuins) metabolize NAD and may have protein ADP-ribosyltransferase activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 260, 273–279 - PubMed
-
- Frye R. (2000) Phylogenetic classification of prokaryotic and eukaryotic Sir2-like proteins. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 273, 793–798 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

