Melatonin inhibits nitric oxide signaling by increasing PDE5 phosphorylation in coronary arteries
- PMID: 23086989
- PMCID: PMC3532536
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00211.2012
Melatonin inhibits nitric oxide signaling by increasing PDE5 phosphorylation in coronary arteries
Abstract
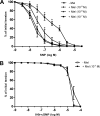
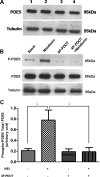
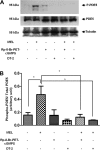
Melatonin inhibits nitric oxide (NO)-induced relaxation of coronary arteries. We tested the hypothesis that melatonin increases the phosphorylation of phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5), which increases the activity of the enzyme and thereby decreases intracellular cGMP accumulation in response to NO and inhibits NO-induced relaxation. Sodium nitroprusside (SNP) and 8-Br-cGMP caused concentration-dependent relaxation of isolated coronary arteries suspended in organ chambers for isometric tension recording. In the presence of melatonin, the concentration-response curve to SNP, but not 8-Br-cGMP, was shifted to the right. The effect of melatonin on SNP-induced relaxation was abolished in the presence of the PDE5 inhibitors zaprinast and sildenafil. Melatonin markedly inhibited the SNP-induced increase in intracellular cGMP in coronary arteries, an effect that was also abolished by zaprinast. Treatment of coronary arteries with melatonin caused a nearly fourfold increase in the phosphorylation of PDE5, which increased the catalytic activity of the enzyme and thereby increased the degradation of cGMP to inactive 5'-GMP. Melatonin-induced PDE5 phosphorylation was markedly attenuated in the presence of the PKG1 inhibitors DT-2 or Rp-8-Br-PET-cGMPS and in those arteries in which PKG1 expression was first downregulated by 24-h incubation with SNP before exposure to melatonin. The selective MT(2) receptor antagonist 4-phenyl-2-propionamidotetralin completely blocked the stimulatory effect of melatonin on PDE5 phosphorylation as well as the inhibitory effect of melatonin on SNP-induced relaxation and intracellular cGMP. Thus, in coronary arteries, melatonin acts via MT(2) receptors and PKG1 to increase PDE5 phosphorylation, resulting in decreased cGMP accumulation in response to NO and impaired NO-induced vasorelaxation.
Figures




Similar articles
-
MT2 receptors mediate the inhibitory effects of melatonin on nitric oxide-induced relaxation of porcine isolated coronary arteries.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011 Jan;336(1):127-33. doi: 10.1124/jpet.110.174482. Epub 2010 Oct 19. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011. PMID: 20959363 Free PMC article.
-
Preservation of nitric oxide-induced relaxation of porcine coronary artery: roles of the dimers of soluble guanylyl cyclase, phosphodiesterase type 5, and cGMP-dependent protein kinase.Pflugers Arch. 2014 Oct;466(10):1999-2008. doi: 10.1007/s00424-014-1441-2. Epub 2014 Jan 12. Pflugers Arch. 2014. PMID: 24413911
-
Celecoxib dilates guinea-pig coronaries and rat aortic rings and amplifies NO/cGMP signaling by PDE5 inhibition.Cardiovasc Res. 2007 Jul 15;75(2):390-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2007.02.026. Epub 2007 Feb 28. Cardiovasc Res. 2007. PMID: 17383621
-
Multimodal action of phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors against neurodegenerative disorders: An update review.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2024 Nov;38(11):e70021. doi: 10.1002/jbt.70021. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39425458 Review.
-
Targeting the NO-cGMP-PDE5 pathway in COVID-19 infection. The DEDALO project.Andrology. 2021 Jan;9(1):33-38. doi: 10.1111/andr.12837. Epub 2020 Jul 3. Andrology. 2021. PMID: 32526061 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effects of Melatonin on the Defense to Acute Hypoxia in Newborn Lambs.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019 Jul 12;10:433. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00433. eCollection 2019. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019. PMID: 31354619 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of mesenteric collecting lymphatic contractions by σ1-receptor activation and nitric oxide production.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2017 Oct 1;313(4):H839-H853. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00702.2016. Epub 2017 Aug 4. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28778917 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclic guanosine monophosphate and the dependent protein kinase regulate lymphatic contractility in rat thoracic duct.J Physiol. 2013 Sep 15;591(18):4549-65. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2013.258681. Epub 2013 Jul 8. J Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23836689 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic benefit of melatonin in refractory central serous chorioretinopathy.Eye (Lond). 2015 Aug;29(8):1036-45. doi: 10.1038/eye.2015.104. Epub 2015 Jul 10. Eye (Lond). 2015. PMID: 26160525 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Interplay Between Melatonin and Nitric Oxide: Mechanisms and Implications in Stroke Pathophysiology.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Jun 13;14(6):724. doi: 10.3390/antiox14060724. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40563356 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Artemyev NO. Binding of transducin to light-activated rhodopsin prevents transducin interaction with the rod cGMP phosphodiesterase gamma-subunit. Biochemistry 36: 4188–4193, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Ballard SA, Gingell CJ, Tang K, Turner LA, Price ME, Naylor AM. Effects of sildenafil on the relaxation of human corpus cavernosum tissue in vitro and on the activities of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase isozymes. J Urol 159: 2164–2171, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Bender AT, Beavo JA. Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases: molecular regulation to clinical use. Pharmacol Rev 58: 488–520, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Boolell M, Allen MJ, Ballard SA, Gepi-Attee S, Muirhead GJ, Naylor AM, Osterloh IH, Gingell C. Sildenafil: an orally active type 5 cyclic GMP-specific phosphodiesterase inhibitor for the treatment of penile erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res 8: 47–52, 1996 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

