Thrombospondin-1 regulates blood flow via CD47 receptor-mediated activation of NADPH oxidase 1
- PMID: 23087362
- PMCID: PMC4394361
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.300031
Thrombospondin-1 regulates blood flow via CD47 receptor-mediated activation of NADPH oxidase 1
Abstract
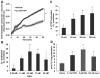
Objective: Although the matricellular protein thrombospondin-1 (TSP1) is highly expressed in the vessel wall in response to injury, its pathophysiological role in the development of vascular disease is poorly understood. This study was designed to test the hypothesis that TSP1 stimulates reactive oxygen species production in vascular smooth muscle cells and induces vascular dysfunction by promoting oxidative stress.
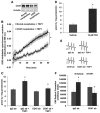
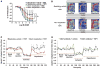
Methods and results: Nanomolar concentrations of TSP1 found in human vascular disease robustly stimulated superoxide (O(2)(•-)) levels in vascular smooth muscle cells at both cellular and tissue level as measured by cytochrome c and electron paramagnetic resonance. A peptide mimicking the C terminus of TSP1 known to specifically bind CD47 recapitulated this response. Transcriptional knockdown of CD47 and a monoclonal inhibitory CD47 antibody abrogated TSP1-triggered O(2)(•-) in vitro and ex vivo. TSP1 treatment of vascular smooth muscle cells activated phospholipase C and protein kinase C, resulting in phosphorylation of the NADPH oxidase organizer subunit p47(phox) and subsequent Nox1 activation, leading to impairment of arterial vasodilatation ex vivo. Further, we observed that blockade of CD47 and NADPH oxidase 1 gene silencing in vivo in rats improves TSP1-induced impairment of tissue blood flow after ischemia reperfusion.
Conclusions: Our data suggest a highly regulated process of reactive oxygen species stimulation and blood flow regulation promoted through a direct TSP1/CD47-mediated activation of Nox1. This is the first report, to our knowledge, of a matricellular protein acting as a ligand for NADPH oxidase activation and through specific engagement of integrin-associated protein CD47.
Figures


References
-
- Bornstein P, Sage EH. Matricellular proteins: extracellular modulators of cell function. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2002;14:608–616. - PubMed
-
- Moura R, Tjwa M, Vandervoort P, Van Kerckhoven S, Holvoet P, Hoylaerts MF. Thrombospondin-1 deficiency accelerates atherosclerotic plaque maturation in ApoE-/- mice. Circ Res. 2008;103:1181–1189. - PubMed
-
- Stenina OI, Krukovets I, Wang K, Zhou Z, Forudi F, Penn MS, Topol EJ, Plow EF. Increased expression of thrombospondin-1 in vessel wall of diabetic Zucker rat. Circulation. 2003;107:3209–3215. - PubMed
-
- Jandeleit-Dahm K, Rumble J, Cox AJ, Kelly DJ, Dziadek M, Cooper ME, Gilbert RE. SPARC gene expression is increased in diabetes-related mesenteric vascular hypertrophy. Microvasc Res. 2000;59:61–71. - PubMed
-
- Lawler JW, Slayter HS, Coligan JE. Isolation and characterization of a high molecular weight glycoprotein from human blood platelets. J Biol Chem. 1978;253:8609–8616. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

